Fig. 16.1
Dissection of the azygos vein – view from the transcervical side
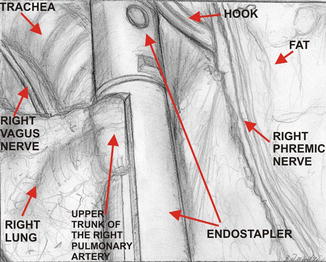
Fig. 16.2
Division of the upper trunk of the right pulmonary artery with endostapler – view from the videothoracoscopic side
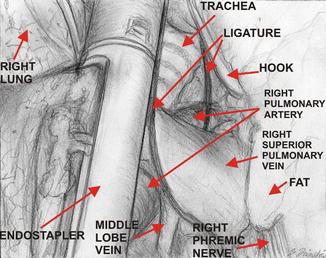
Fig. 16.3
Division of the upper trunk of the right pulmonary vein with endostapler – view from the videothoracoscopic side
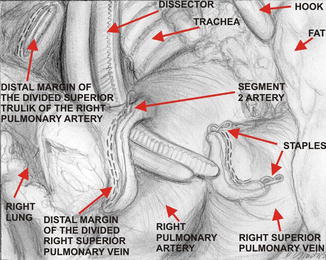
Fig. 16.4
Closure of segment 2 artery with vascular clips – view from the videothoracoscopic side
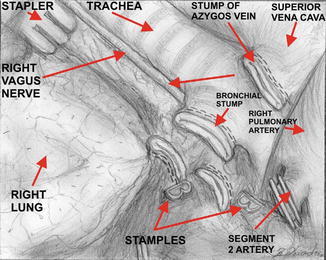
Fig. 16.5
Division of the right upper lobe bronchus – view from the videothoracoscopic side
16.4.2 Left Upper Lobectomy
The operative procedure is performed under general anesthesia with the use of right intrabronchial intubation for selective lung ventilation. The initial step is TEMLA with excision of nodal stations 1, 2R, 4R, 2L, 4L, 7, 8, 5, and 6 with intraoperative imprint cytology analysis of the nodes. The dissection of the aortopulmonary (AP) window area containing stations 5 and 6 nodes is performed with the use of AP window retractors (Fig. 16.6). The retractors are critically important for performance of the subsequent left upper lobectomy enabling wide access to the left pleural cavity. After obtaining negative results from the examination of all nodes, ventilation of the left lung is disconnected and right lung ventilation is started. The left mediastinal pleura is divided in front of the left phrenic nerve which creates a wide access to the left part of the chest. Two VATS ports are inserted, one for the videothoracoscope and the other one for endostaplers. The whole dissection is performed in the open fashion through the transcervical incision under control of VATS camera. Dissection of the left upper pulmonary vein is started first. The dissected vein is divided with endostapler (Fig. 16.7). The next dissected structure is the first branch of the left pulmonary artery, which is subsequently double ligated and divided or managed with endostapler (Fig. 16.8). The third dissected structure is the left upper lobe bronchus (Fig. 16.9) which is divided with endostapler. The other two or three branches of the pulmonary artery are double ligated or double clipped and divided through the transcervical incision (Fig. 16.10). The interlobar fissure is divided with endostapler and the lobe is extracted from the chest in an endobag. Lymphadenectomy of the stations 10, 11, and 12 is completed. The pulmonary ligament is divided. Hemostasis is checked and a single 24–28 Ch chest tube is inserted through the incision for the VATS port. The transcervical incision is closed in the standard fashion without any other drain.




