Fig. 13.1
Dissection of the left innominate vein from the inner surface of sternum after elevation of the manubrium with a hook connected to the Rochard frame
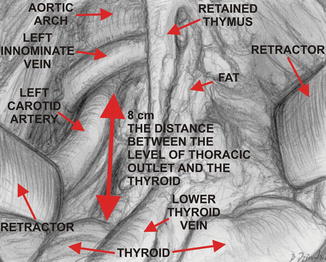
Fig. 13.2
View of the retained part of the left upper pole of the thymus after previous unilateral VATS thymectomy
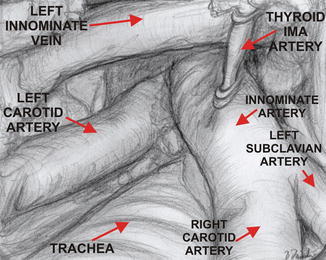
Fig. 13.3
The view of the great mediastinal vessels from the transcervical incision. The atypical thyroid ima artery was clipped and divided
13.5 Results
The sole transcervical technique was used for rethymectomy in 3 patients, and the transcervical-subxiphoid-bilateral VATS maximal rethymectomy was used in 2 patients at our institution. These were 5 patients who had undergone previous unilateral VATS thymectomy elsewhere. Part of the upper poles of the thymus was discovered in all patients on rethymectomy. It might confirm a potential incompleteness of the unilateral VATS thymectomy as was described by Shigemura et al. [1]. Our results of follow-up of patients who underwent rethymectomy showed complete remission in 1/5 patients and improvement in 4/5 patients after a follow-up of 22–72 months (mean 51 months). The results of this small group, taken together with the results of our previous study with patients undergoing rethymectomy through resternotomy, show that for unknown reasons the repeated operation is much less effective than the primary procedures. They also stress the necessity to perform the initial thymectomy in the best possible way, preferably in the extended fashion with complete removal of the whole thymus and the surrounding fatty tissue.
The advantage of rethymectomy in our patients was the possibility to wean most of them from steroids and immunosuppressive medication.
13.6 Complications
We experienced no intraoperative or postoperative complications in our patients undergoing transcervical rethymectomy.
13.7 Conclusions
1.




Rethymectomy can be safely performed with a minimally invasive technique such as the transcervical approach used either solely or in combination with VATS and/or a subxiphoid incision.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


