Fig. 19.1
This 12 lead EKG tracing demonstrates a heart in normal sinus rhythm. There is possible inferolateral ischemia demonstrated by the T wave inversions in II, III, and AVF and V4-V6. Note the particularly tall QRS complexes in V4-V6 indicating left ventricular hypertrophy. Such hypertrophy can result in the S4 heart sound
Echocardiogram (Fig. 19.2) shows left ventricular hypertrophy, with a wall thickness of 1.3–1.5 cm.
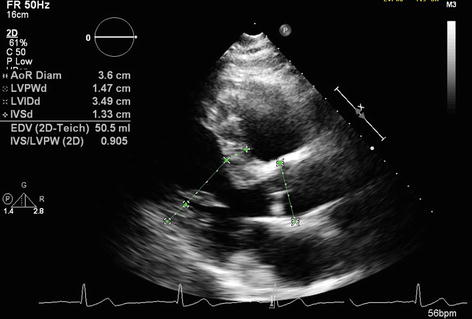

Fig. 19.2
This is an echocardiogram displaying the ventricles of the heart. Note the thickened ventricular walls consistent with the S4 heart sound and EKG findings
Clinical Basics
Pathophysiology of S4
End diastolic ventricular filling normally occurs as the atria contract to provide extra stretch to the ventricles. Stiffening of the ventricles, caused by ventricular hypertrophy, infarction, or fibrosis, reflexively evokes a more vigorous atrial contraction in order to overcome this reduced ventricular compliance. The S4 gallop occurs as the accelerated column of blood decelerates against the stiff ventricular walls. See Fig. 19.3.
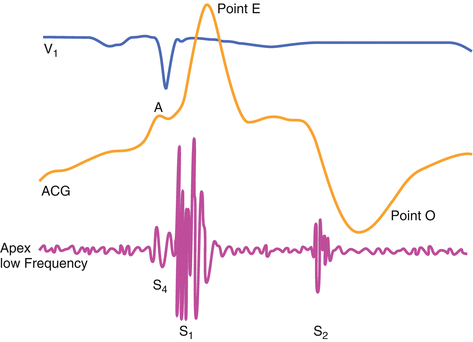
Fig. 19.3
The diagram illustrates the presystolic nature of an S4 as well as its proximity to S1. It is subtle low frequency sound
The conditions required for S4 formation include:
Reduced ventricular compliance.
Healthy atrium.
Regular sinus rhythm.
The absence of atrioventricular (AV) valve dysfunction.
Certain pathologies associated with reduced ventricular compliance, and therefore the possible presence of an S4 gallop include:
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), as caused by hypertension or left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction.
Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), as caused by pulmonary hypertension or right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) obstruction.
Ischemic heart disease.
Aortic stenosis.
An S4 may also be heard in older patients with age-related ventricular hypertrophy or in well-trained athletes with physiologic ventricular hypertrophy.
Key Auscultation Features
The S4 gallop is a low frequency (10–50 Hz), presystolic heart sound best detected at the left ventricular apex.
Use the bell of the stethoscope.
Accentuate the S4 by placing the patient in the left lateral decubitus position.
Increased heart rate will shorten the PR interval and cause the S4-S1 interval to shorten and possibly merge (Fig. 19.4).
< div class='tao-gold-member'>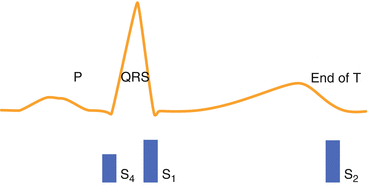 Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


