Fig. 4.2 (a) Timing and size of the contribution of right and left atria to the shape of the P wave. Right atrial depolarization occurs first, and occupies the first two-thirds of the P wave; left atrial depolarization onset is delayed by about one-third of the duration of the P wave, and then occupies the remaining two-thirds. In health, both contribute equally to the size of the P wave. Thus the first and last thirds of atrial depolarization are exclusively the domain of the right and left atria. Both atria contribute to the middle third of the P wave and hence in health the overall P wave is largest in the middle of the P wave. (b) P wave shape in leads II and V1; both left and right atrial depolarization are directed towards lead II. Right atrial depolarization is directed towards lead V1, though left atrial depolarization is largely away, accounting for the appearance of a late but small negative P wave deflection in lead V1.
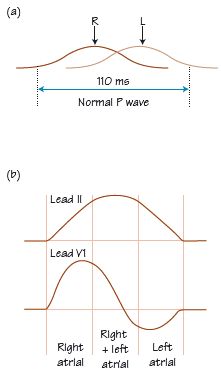
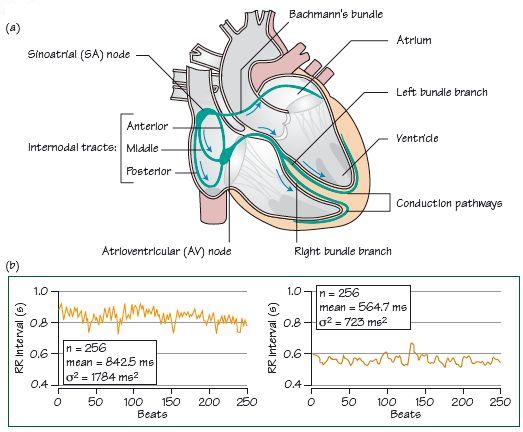
Fig. 4.3 (a) Atrial depolarization, which starts at the sinus node, spreads down internodal and interatrial (‘bundle of Bachmann’) pathways, respectively allowing for right and left atrial depolarization. The impulse then proceeds into the atrioventricular [AV] node and the rest of the heart. (b) Heart rate variability. Two traces of RR interval (essentially the same as PP interval) plotted out against beat number (i.e. instantaneous heart rate). Left lying, right tilted up. Vagal tone, higher when lying, increases high-frequency heart rate variability (σ2, measured in milliseconds squared), seen as instantaneous increases/decreases in RR interval (sharp ‘spikes’ on the tachogram). Standing increases sympathetic tone, increasing heart rate (i.e. lessening RR interval) as vagal tone is withdrawn, lessening the high-frequency changes seen when lying (n = number of beats assessed, μ = average RR interval). (c) Trace of heart rate (HR) plotted out against time from a normal 24-h ECG; normal heart rate variability, with a clear decrease in heart rate at night when asleep.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


