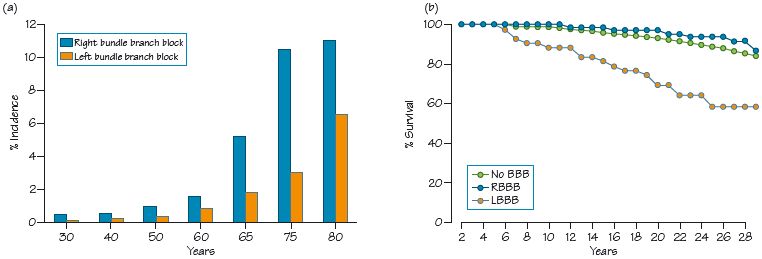
Fig. 53.2 Left bundle branch block (LBBB). Sinus rhythm, normal P wave, PR interval. Broad QRS > 120 ms, broad negative deflection in lead V1, broad positive deflection with a slurred upstroke in lead V6. Deep S waves inferiorly, a consequence of LBBB. Inverted T waves laterally (I, aVL, V5, V6), a consequence of the very slow depolarization of the left ventricle reversing the normal repolarization sequence.
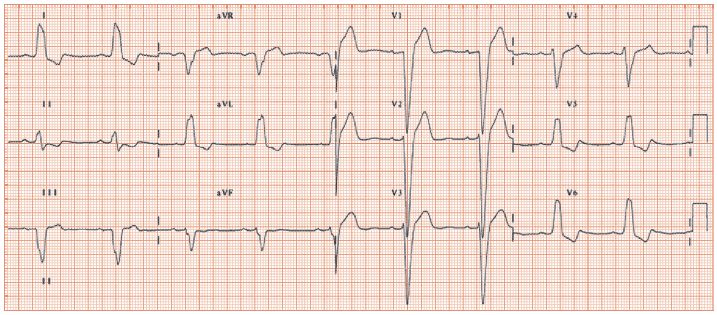
Fig. 53.3 (a) Age-specific incidence of bundle branch block (BBB). BBB increases with age, and at any age right bundle branch block (RBBB) is commoner than left (LBBB). (b) Prognosis of BBB.
Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a common conduction disturbance, with three distinct patterns of damage:
- Damage to one or other (but not both) of the two major subdivisions of the left bundle (see Chapter 10). Blockage results in QRS axis deviation without QRS broadening (left axis deviation with anterior hemi-fascicular block, right axis deviation with posterior hemi-fascicular block).
- Partial LBBB (‘incomplete LBBB’) has some but not all of the features of full LBBB, and is the consequence of partial rather than full interference with the function of the left bundle. The commonest finding is disappearance of the left side physiological septal Q waves with slight broadening of the QRS complex, which is still ≤ 120 ms. In time, this usually progresses to full LBBB.
Full LBBB
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


