Fig. 42.2 An atrial extrasystole (red arrow), occurring on the top the T wave, resulting in an early QRST complex. Most atrial extrasystoles reset the sinus node, this does not happen here and the extrasystole is followed at the appropriate time by another P wave, the timing affected by the extrasystole.
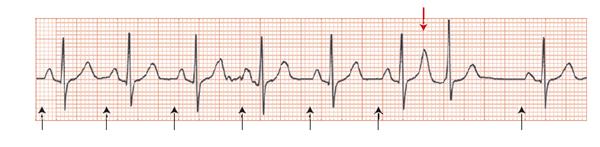
Fig. 42.3 Ectopic atrial tachycardia; well defined frequent P waves, too fast to be sinus, with block, every 4–6 atrial beats gets through to activate the ventricle. These P waves are best seen in leads I, aVR, V1. Their shape is very different from a normal sinus rhythm P wave. In some leads, e.g. III, aVF, and the lateral chest leads, they appear irregular and of small voltage, and could easily be confused with atrial fibrillation. The QRS complexes are normal and there is lateral T wave flattening.
Atrial ectopic beats are extremely common. The features of atrial extrasystoles are:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


