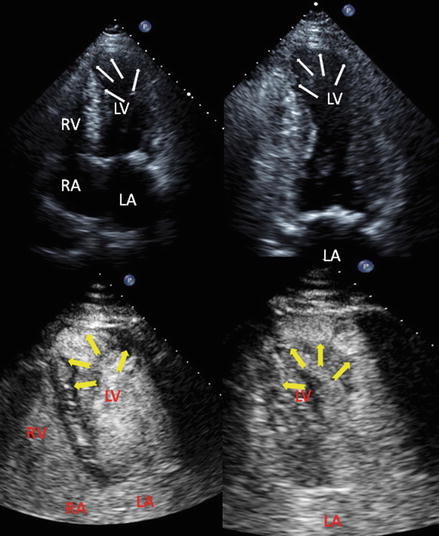
Figure 14.1
Parasternal long (left) and apical four chamber (right) views of a patient with Amyloidosis. Please notice thickened walls of both ventricles, speckled appearance of myocardium (better seen in the interventricular septum), biatrial enlargement and mild valve thickening
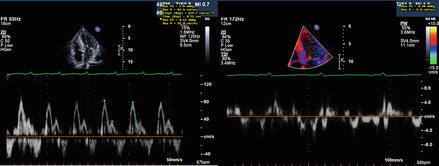
Figure 14.2
Mitral inflow pattern (left) and tissue Doppler (right) of patient with amyloidosis showing restrictive physiology
1.
Types of amyloid
AL – Primary amyloidosis, light chain deposition
AA – Secondary amyloid, deposition of part of acute phase protein (AA)
Familial amyloidosis – multiple types including transthyretin mutation (ATTR), apolipoprotein A-I and A-II, fibrinogen (AFib), lysozyme (L)
Beta-2 microglobulin. Beta-2 microglobulin does not get excreted by kidneys
Localized versions (many types) – including localized dystrophic amyloidosis of heart valves, senile atrial amyloidosis of the heart (Atrial natriuretic peptide)
2.
Cardiac involvement may occur in the following types of amyloidosis:
in AL and ATTR cardiac involvement is a major source of morbidity and mortality
AA
3.
Presenting features:
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Arrhythmias (both atrial and ventricular)
AV blocks and other conduction defects
Pleural and pericardial effusions
Ischemia from microvascular deposition of material
Intra-cardiac thrombi (both atrial and ventricular)
Low voltage on ECG and hypertrophied myocardium on echo
4.
Echocardiography finding (note: they are very variable depending on stage of amyloidosis)
Left ventricular thickening, concentric. RV is often involved
Poor function of both ventricles
Diastolic dysfunction
Biatrial enlargement
Speckled appearance of myocardium (note – this depends on gain settings)
Valvular thickening
Strain and strain rate abnormalities (long axis dysfunction is apparent even in early stages of amyloidosis)
Chagas Disease (Fig. 14.3)
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


