(1)
The Lindner Center for Research and Education The Christ Hospital, The Christ Hospital Physicians Ohio Heart and Vascular Center, Cincinnati, OH, USA
Keywords
Left dominantRight dominantCircumflex coronary arteryCxLeft anterior descending coronary arteryLADDiagonalObtuse marginalOMRight ventricular marginalRV marginalRight coronary arteryRCAConus arteryAV nodal branchRight ventricleRVLeft ventricleLVLeft atriumLARight atriumRACoronary sinusLeft atrial appendagePosterior descending arteryPDALeft posterior descending arteryRight posterior descending arteryMiddle cardiac veinPosterolateral cardiac veinSuperior vena cavaInferior vena cavaRight pulmonary arteryLeft pulmonary arteryPulmonary arteryRight atrial appendageRight ventricular outflow tractLeft main coronary arteryLMAtrioventricular valvesMitral valveTricuspid valveAortic valvePulmonary valveAzygous veinAortaAscending aortaDescending aortaAtrio-ventricular groovePosterolateral coronary arteryCoronary sinusLeft coronary sinusNoncoronary sinusRight coronary sinusLeft coronary cuspRight coronary cuspNoncoronary cuspRamus intermedius coronary arteryPulmonary veinsLeft upper pulmonary veinLeft lower pulmonary veinRight upper pulmonary veinRight lower pulmonary veinSeptal branchesGreat cardiac veinPosterior veinVein of marshallSmall cardiac veinMiddle cardiac veinAnterior cardiac veinAnterior interventricular veinLateral marginal veinAccurate cardiac computed tomographic angiography (CCTA) interpretation mandates a thorough understanding of cardiac anatomy. CCTA affords the opportunity to visualize the heart and great vessels in exquisite detail. What follows is a general overview of pertinent normal cardiac anatomy.
Figure 4.1 depicts a volume rendered (VRT) CCTA image of a left dominant, normal heart viewed from multiple anatomic positions. Panel A is an anterior depiction. Panel B is a posterior representation. Panel C is a right anterior oblique view and panel D is posterior illustration viewed from a cranial perspective. In panel A, note the anterior lying right ventricle, right ventricular outflow tract and pulmonary artery. The left anterior descending artery (LAD) runs in the anterior interventricular groove. Note the multi-lobular left atrial appendage (LAA) lying over the circumflex coronary artery (CX). Panel B illustrates the posteriorly oriented left atrium (LA), pulmonary veins (PV) and left ventricle (LV) as well as the dominant CX travelling in the atrio-ventricular groove and giving rise to an obtuse marginal vessel (OM) and the left posterior descending coronary artery (LPDA). Note the less opacified coronary sinus (CS) emanating from the right atrium (RA) and giving rise to the take off of the middle cardiac vein (MCV) which runs aside the LPDA and a posterolateral cardiac vein (PLV) paralleling the OM. Panel C depicts the nondominant Right Coronary Artery (RCA) and its Right Ventricular Marginal artery (RVM). Note the Superior Vena Cava (SVC) running parallel to the ascending aorta (AO) and connecting to the RA. Panel D nicely demonstrates the primary branching of the PA into the right pulmonary artery (RPA) and left pulmonary artery (LPA). In addition, this orientation clearly depicts the pulmonary veins. Note that the right atrial appendage (RAA) is larger and smoother than the LAA.
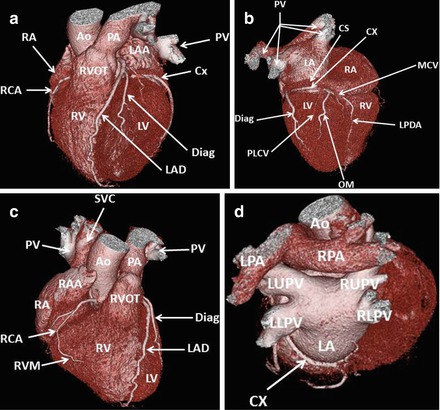





Figure 4.1
A volume rendered (VRT) image of the normal cardiac anatomy in a left dominant heart. Panel (a) is an anterior view. Panel (b) is a posterior illustration. Panel (c) is a right anterior oblique image and panel (d) is a posterior view in a cranial orientation. RA Right atrium, RCA right coronary artery, RV right ventricle, RVOT right ventricular outflow tract, AO ascending aorta, PA pulmonary artery, LAA left atrial appendage, PV pulmonary veins, CX circumflex coronary artery, LV left ventricle, LAD left anterior descending coronary artery. Diag diagonal coronary artery, CS coronary sinus, MCV middle cardiac vein, PLCV posterolateral cardiac vein, LPDA left posterior descending coronary artery, SVC superior vena cava, RVM right ventricular marginal coronary artery, RPA right pulmonary artery, LPA left pulmonary artery, LUPV left upper pulmonary vein, LLPV left lower pulmonary vein, RUPV right upper pulmonary vein, RLPV right lower pulmonary vein
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


