, where c – speed of sound λ – wavelength, υ – frequency
Speed in media is proportional to density and elasticity (which is proportional to temperature). Thus sound travels faster in soft tissue than air and faster in metal than soft tissue.
Ultrasound waves can reflect and refract when they are interacting borders between different media (Fig. 1.1)
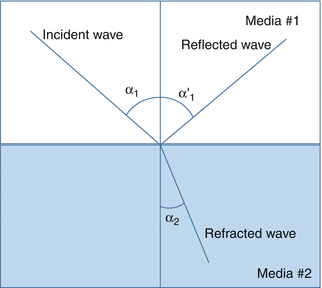

Figure 1.1
Ultrasound waves both reflect and refract when they come to border between two media with different physical properties
Transducer can be focused only in near field
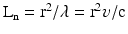 , Where Ln – length of near field, λ – wavelength, υ – frequency, r – radius of the transducer, c- speed of sound in media
, Where Ln – length of near field, λ – wavelength, υ – frequency, r – radius of the transducer, c- speed of sound in mediaSin α = 0.61/r – divergence of beam in the far field
Snell’s law: calculates angle of refraction
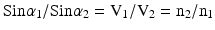 where n is index of refraction
where n is index of refractionSpatial Resolution: refers to the smallest distance in which 2 points can be distinguished as separate. There are two types of spatial resolution; axial and lateral (Fig. 1.2).
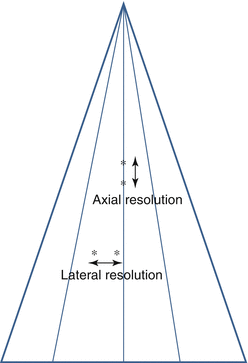

Figure 1.2
Definition of axial and lateral resolution
Axial resolution: refers to ability to resolve 2 points in the direction of the ultrasound beam (axial direction or depth); proportional to λ, υ, and duration of transmitted pulse. Typical axial resolution for cardiac ultrasound is
Lateral resolution: refers to ability to resolve 2 points in a perpendicular plane from the ultrasound beam (along the sides of the beam); proportional to beam width
Temporal Resolution: refers to ability to resolve 2 points that has moved over time; is quantified as the frame rate; frame rates can be improved by narrowing imaging sector, decreasing depth, and decreasing line density
Absorption: refers to when sound amplitude is weakened due to inner friction (viscosity)
Energy transferred to heat
Scattering occurs at all the interfaces
Attenuation refers to decrease in sound amplitude from reflection of sound wave
Attenuation increases as frequency of sound wave increases (can reflect off smaller interfaces)
Half value level – distance sound travels before intensity goes to 50 %
In tissue attenuation is 1 dB/cm/MHz
Transducer
Transducers contain piezoelectric elements which are made of metallic crystals that can transfer sound waves to electric signals and vice versa. These physical elements are responsible for the mechanoelectric transduction of ultrasound to electric data.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


