Thymic Carcinoma
Presentation
A 53-year-old-man presents to his primary care physician complaining of weight loss, chest pain, and cough. On physical examination, the physician notes decreased breath sounds over the left chest. X-rays are performed, and the patient is referred to your office.
▪ Chest X-rays
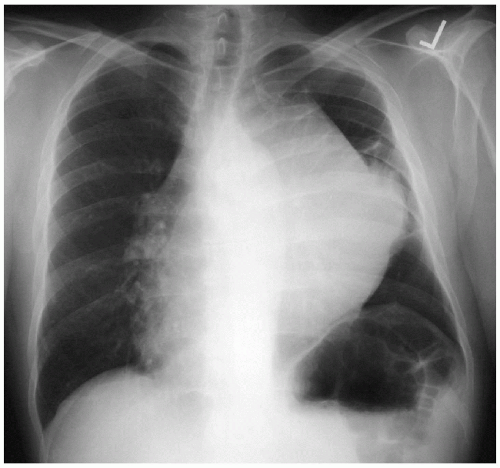
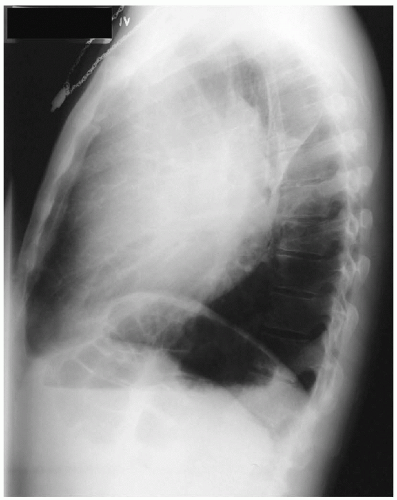
Chest X-ray Report
There is a large anterior mediastinal mass projecting to the left side. There is atelectasis of portions of the left lung. The cardiac contour and trachea are displaced to the right side. On the lateral x-ray, the left hemidiaphragm is elevated, which also suggests volume loss, possibly owing to atelectasis in the left lung or diaphragmatic paralysis. ▪
Differential Diagnosis
The major lesions occurring in the anterior mediastinum in the adult include thymoma, lymphoma, thyroid goiter, and germ cell tumors. Less commonly, mediastinal masses may be tumors of vascular or mesenchymal origin or displaced parathyroid tissue.
Discussion
The mediastinum is generally divided into three compartments: the anterior compartment, the visceral compartment, and the paravertebral sulci. The innominate vessels limit the anterior compartment superiorly, with the heart and great vessels limiting it posteriorly. At the thoracic inlet, only the visceral and paravertebral compartments are found. All three compartments extend to the diaphragm. The mediastinal surface of the parietal pleura limits all three compartments laterally.
As mentioned earlier, the major tumors occurring in the anterior mediastinum are thymomas, lymphomas, germ cell tumors, and thyroid goiter. In the visceral compartment, foregut cysts (bronchogenic, esophageal, and gastric) and primary as well as secondary tumors of the lymph nodes constitute most of the masses in this compartment. Also included in visceral compartment masses are pleuropericardial cysts. Most masses arising in the paravertebral sulci are tumors of neurogenic origin (Table 38-1).
In infants and children, the most common masses, in decreasing order of frequency, are neurogenic tumors, enterogenous (foregut) cysts, germ cell tumors, lymphomas, angiomas and lymphangiomas, thymic tumors, and pericardial cysts. In adults, the most common masses, in decreasing order of frequency, are
thymic tumors, neurogenic tumors, lymphomas, germ cell tumors, foregut cysts, and pericardial cysts.
thymic tumors, neurogenic tumors, lymphomas, germ cell tumors, foregut cysts, and pericardial cysts.
Table 38-1: Primary Tumors and Cysts of the Mediastinum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree