Fig. 49.2 Differing ECG appearance in lead V1 indicating ventricular tachycardia (VT). Right bundle branch block (A) shows a rsR′ pattern; all the other patterns (B to F) suggest VT. A dominant QRS complex in lead V1 suggests that the VT is left ventricular in origin. If there is also left axis deviation, consider the rare diagnosis of fascicular tachycardia. (C) The V1 QRS complex is sometimes described as rabbit ears in VT (C), with the left (from behind) being larger than the right, the reverse of right bundle branch block (A).
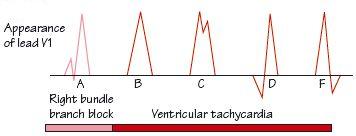
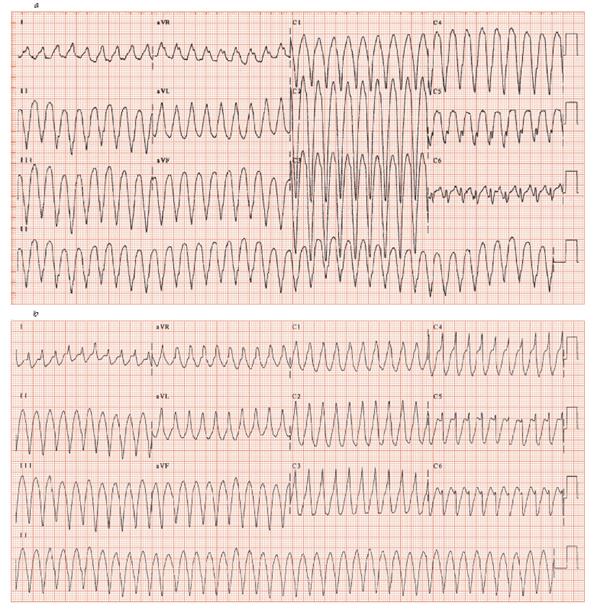
Fig. 49.3 (a) Broad complex tachycardia. The rate is very fast, about 220 b/min. There are no clear cut P waves, but running your eye along the rhythm trace at the bottom, slight irregularities can be occasionally seen, which are likely to be P waves. The axis is extreme rightward (+ve aVR, aVL). The complexes are very broad. All the chest lead R waves are negative (‘praecordial concordance’). On ECG grounds this clearly ventricular tachycardia (VT), of right ventricular origin (confirmed by knowing the patient had Fallot’s tetralogy). (b) Broad complex tachycardia, rate 250 b/min, suggestive but no clear cut irregularities on the rhythm trace suggesting independent P wave activity. No praecordial concordance (QRS +ve in V1–3, –ve in V4–6), but QRS very broad (143 ms), QRS shape in lead V1 like (B) in Fig. 49.2, both strongly suggest VT. The diagnosis was post-myocardial infarction VT.
Monomorphic (‘one shape’) ventricular tachycardia (VT) is common, serious and has many causes (Table 49.1), most often a scar allowing ‘re-entry’ (Fig. 49.1) and so the development of a ‘circus movement’ tachycardia (a re-entrant arrhythmia), the electrophysiological characteristics of which are:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


