INDICATIONS/CONTRAINDICATIONS
Historical indications for the Monaldi procedure include decompression of post-tuberculous and pyogenic pulmonary abscess cavities. Image-guided percutaneous drainage has become the treatment of choice for pulmonary abscesses that do not resolve with systemic antibiotics.
The modified Monaldi procedure for giant bullous emphysema (Brompton technique) is currently indicated for patients meeting the following criteria:
1. Dominant, discrete bullous lung disease encompassing 30% or more of the pleural space and with functional surrounding lung parenchyma.
a. The cyst should have a small number of septations to ensure complete drainage with one or two drainage catheters.
2. Disabling dyspnea.
Absolute contraindications for a modified Monaldi procedure include:
1. No viable or functional lung surrounding the bulla.
2. Diffuse, nonparaseptal emphysema.
Relative contraindications include:
1. Mild symptoms
2. FEV1 less than 350 mL (due to higher mortality risk)
 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING
PREOPERATIVE PLANNING
Evaluation includes history and physical examination, documentation of severity of dyspnea and pulmonary impairment and smoking cessation. Pulmonary rehabilitation for up to 6 weeks with deep breathing exercises, coughing exercises, incentive spirometry, and out-of-bed activity has been shown to be beneficial in preoperative patients with advanced emphysema.
Preoperative workup includes:
1. Chest radiograph
2. CT scan of the chest
3. Pulmonary function tests (including lung volumes by whole body plethysmography, spirometry, and diffusion capacity)
4. Arterial blood gas
The most important aspect of the preoperative plan is selecting the appropriate patients based on severity of symptoms and CT imaging. Patients with dominant giant bulla with limited septations and compressed functional lung tissue are the ideal candidates for this procedure (Fig. 8.1).
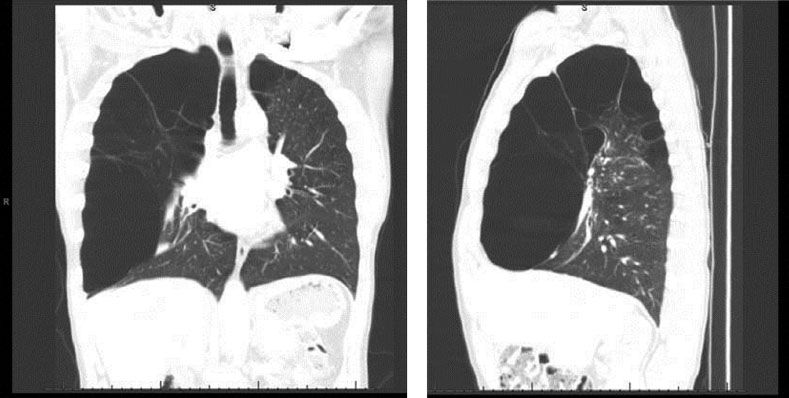
Figure 8.1 Sagittal and coronal computed tomography images of the chest demonstrating a giant bulla compressing the right lower lobe and flattening the diaphragm.
 SURGERY
SURGERY
The airway strategy is flexible with the modified Monaldi procedure and depends on the ability of the patient to tolerate single lung ventilation. Airway management strategies include:
1. Spontaneous breathing with local anesthetic
2. Double lung ventilation via single-lumen tube
3. Double lung ventilation via single-lumen tube with intermittent apnea
4. Single lung ventilation via double-lumen tube or bronchial blocker
Fiberoptic bronchoscopy may be performed to assess the anatomy of the tracheobronchial tree and obtain cultures.
Positioning
The patient is placed in the optimal position to provide access to the bulla. The location of the incision is based on CT imaging and can be landmarked by the specific interspace or rib overlying the bulla.
Technique of the Modified Monaldi Procedure
The operative steps for the single-stage modified Monaldi procedure for decompression of giant bullae are:
1. A small incision is made directly over the most dependent portion of the bulla as determined by preoperative imaging or with assistance of thoracoscopy (Fig. 8.2).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


