Erratum for Bays. “Adiposopathy, Diabetes Mellitus, and Primary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Coronary Artery Disease: Treating “Sick Fat” Through Improving Fat Function with Antidiabetes Therapies” Am J Cardiol 2012;110(9S):4B–12B.
The publisher regrets that due to a typesetting error, Figure 1 contained the following error: an inaccurate portrayal of the hypothalamic regions. See below for the correct figure. The figure was correctly supplied by the author.
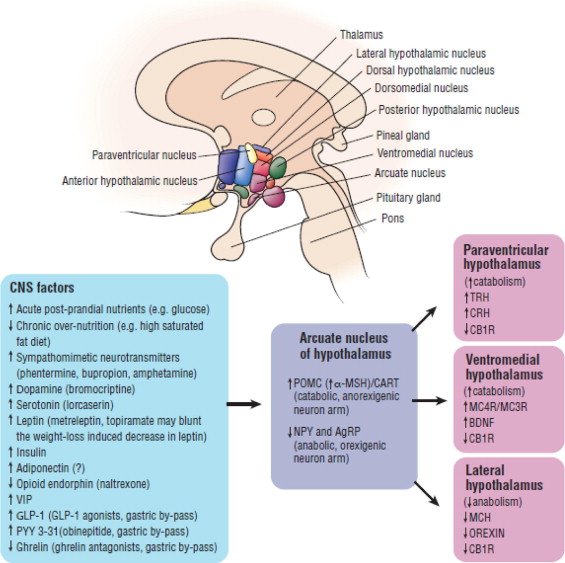
Simplified relation between selected central nervous system factors on anorexigenic and orexigenic effectors within the hypothalamus. Legend: Regarding central nervous system (CNS) factors, up arrows mean that an increase in the listed CNS factor increases arcuate nucleus POMC/CART activity and/or decreases NPY and/or AgRP activity, and thus increases catabolism and/or decreases anabolism. A down arrow means that a decrease in the CNS factor also increases catabolism and/or decreases anabolism via the arcuate nucleus. Increased anorexigenic POMC (which is cleaved to form melanocortins such as MSH) and CART expression, and decreased orexigenic expression of NPY and AgRP contribute to “second-order” signaling through arcuate nucleus neuron projection to other hypothalamic regions. The net result is increased anorexigenic and increased catabolic effects, and decreased orexigenic and decreased anabolic effects. This figure is greatly simplified, does not show all the interconnected signaling pathways between these CNS factors, and the reported effects of these CNS factors on POMC and NPY are not always consistent. An acute postmeal increase in glucose (not necessarily hyperglycemia) stimulates the arcuate nucleus. Chronic over-nutrition (especially with high saturated fat diet) may cause hypothalamic injury with impaired satiety signaling that may promote further positive caloric balance and adiposity. 30,31 A lack of chronic over-nutrition may avoid hypothalamic injury, and thus improve or maintain arcuate nucleus neuronal function with respect to catabolism and anabolism, and thus improve or maintain adipocyte and adipose tissue function. AgRP = agouti-related peptide; BDNF = brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CART = cocaine amphetamine-regulated transcript; CB1R = cannabinoid 1 receptor; CRH = corticotropin-releasing hormone; GLP-1 = glucagon-like peptide-1; MC3R = melanocortin 3 receptor; MC4R = melanocortin 4 receptor; MCH = melanin-concentrating hormone; MSH = melanocyte-stimulating hormone; NPY = neuropeptide Y; POMC = pro-opiomelanocortin; PYY 3 -31 = peptide YY; TRH = thyroid-releasing hormone; VIP = vasoactive intestinal peptide.

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


