Coagulation and Thrombosis The coagulation cascade as described in manuscripts is an over simplification of a very complex phenomenon. Traditionally this cascade has been divided into intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. However, both these pathways are in fact intimately linked. The extrinsic pathway is the most important pathway in vivo! Antithrombin (AT). This inhibits factor Xa and thrombin by acting as a suicide substrate. It also works in conjunction with heparin cofactor II, which also has a direct inhibitory effect on thrombin. Proteins C and S. These are activated by thrombin and degrade cofactors Va and VIIIa, thereby diminishing the activation of prothrombin and FX. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI). This binds to and inhibits factor Xa and the factor VIIa-tissue factor complex. tPA
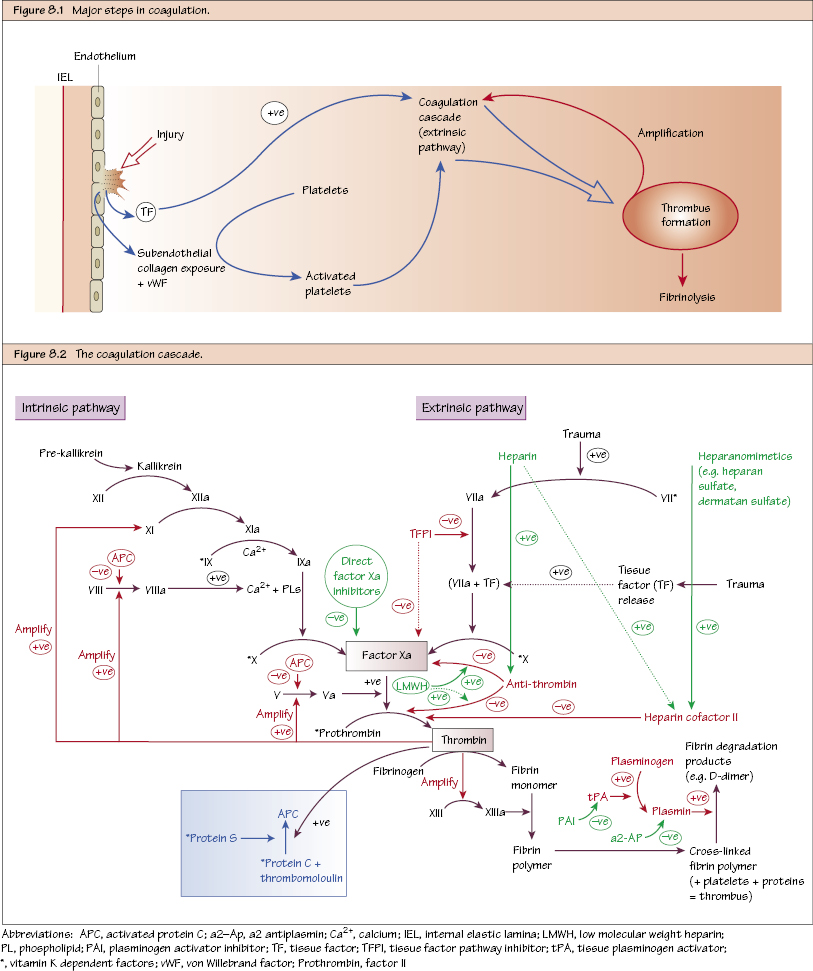
Steps in Coagulation
Steps in the Coagulation Cascade
Inhibitory Pathways
Fibrinolysis Pathway
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


