Fig. 24.1
Typical crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur of an ASD
Grade 1 crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur.
Fixed, split S2 heard at the RUSB.
An S3 gallop was noted at the lower left sternal border.
Test Results
His electrocardiogram showed a right axis RBBB (Fig. 24.2).
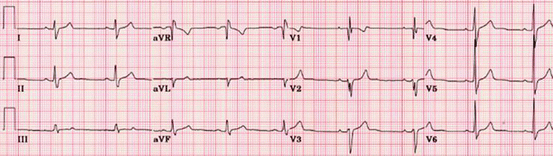
Fig. 24.2
Right bundle branch block (RBBB) on electrocardiogram
Chest radiography showed a prominent pulmonary artery and mild right ventricular enlargement (Fig. 24.3a, b).
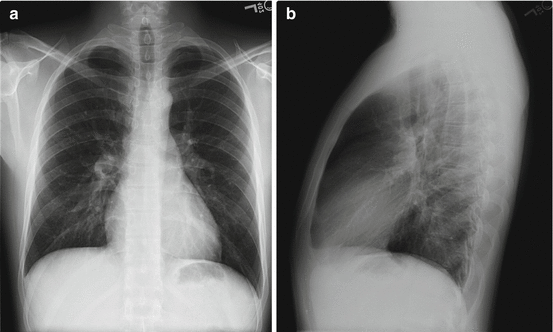
Fig. 24.3
(a, b) Prominent pulmonary artery and right ventricular enlargement. (a) PA chest radiograph. (b) Lateral chest radiograph
Hand x-rays show mild thenar abnormalities, but grossly radiographically normal (Fig. 24.4).
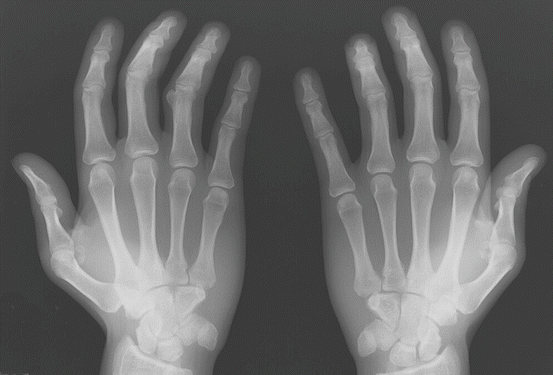
Fig. 24.4
Mild thenar abnormalities of the hands
Echocardiography showed right atrial and right ventricular enlargement (Fig. 24.5). There was also left to right flow across the atrial septum. A Doppler demonstrated that the left to right flow begins in mid systole and continues to early diastole at a rate of 1 m/s (Fig. 24.6).
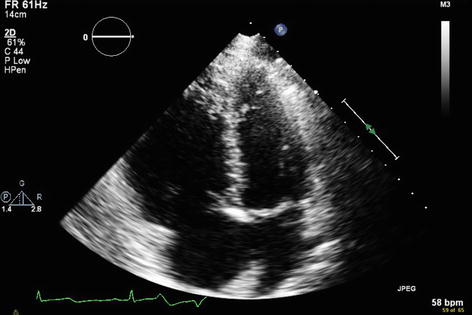
Fig. 24.5
Echocardiography demonstrating right atrial and right ventricular enlargement
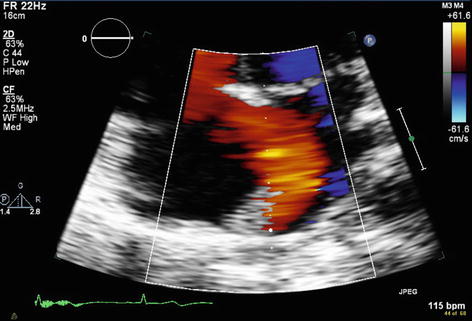
Fig. 24.6
Left to right flow on Doppler echocardiogram
A right heart catheterization showed normal right heart pressures, a pulmonary artery pressure of 24/10 mmHg, and an increased ratio of pulmonary to systemic flow (Qp/Qs) of 2.6:1.
Clinical Basics
Definition
There are four subtypes of ASD, in decreasing order of frequency (Fig. 24.7):
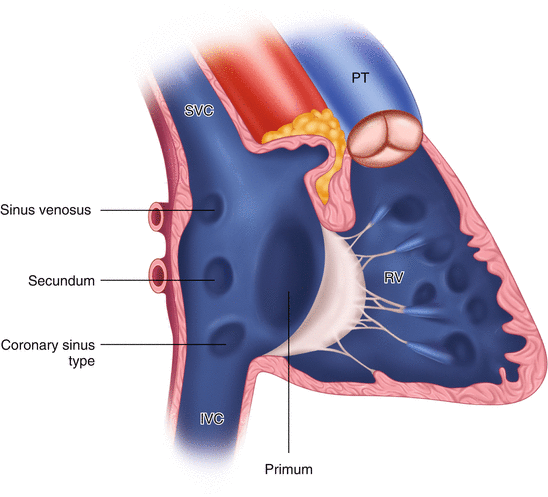

Fig. 24.7
Location of atrial septal defects
Secundum- the most common and arising in the fossa ovalis.
Primum ASD is often associated with mitral regurgitation.
Sinus venosus ASD is associated with an anomalous pulmonary venous return.
Coronary sinus type (uncommon).
Symptoms of ASD
Symptoms of ASD range from asymptomatic to palpitations, dyspnea, and fatigue. Palpitations are a common symptom in patients with ASD and are often secondary to the right ventricular impulse seen with volume overload.
Prevalence
This defect is the third most common form of congenital heart disease.
Clinical syndromes associated with ASD include:
Hand-Heart syndrome. There can be mild upper limb thenar and carpal functional abnormalities that can appear normal on radiograph. ASD is the most common cardiac finding associated with hand-heart syndrome in 70 % of cases. There may be a genetic basis to this syndrome, but it is heterogeneous with variable penetration.
Holt-Oram syndrome is another associated clinical finding of ASD. It is an autosomal dominant disease associated with limb and cardiac abnormalities.< div class='tao-gold-member'>Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


