Axial aortorenal endarterectomy is the most common direct method of restoring renal blood flow in cases of aortic spillover plaque (Figure 1). Before occluding the aorta, the proximal superior mesenteric artery and distal renal arteries are clamped to prevent embolization of atheromatous debris from the aorta. These vessels are controlled using low-pressure (30–70 g) microvascular Heifitz clamps. Aortic control is obtained proximally just above the superior mesenteric artery and 3 to 4 cm below the level of the renal arteries. Aortic occlusion is occasionally required above the level of the celiac artery when the distance for clamping between the superior mesenteric and renal arteries is short.
Transaortic Renal Artery Endarterectomy for Renal Artery Atherosclerosis
Operative Technique
Exposure
Axial Aortorenal Endarterectomy
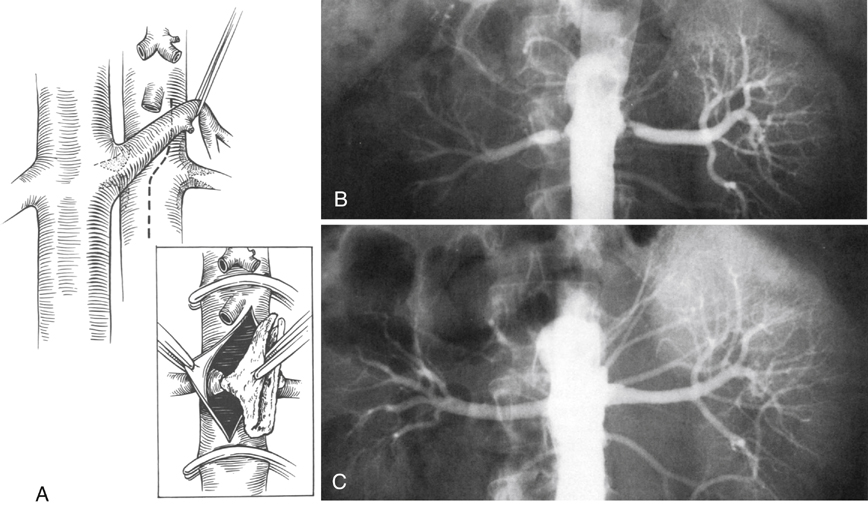
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Transaortic Renal Artery Endarterectomy for Renal Artery Atherosclerosis
