Tracheal Narrowing
Jud W. Gurney, MD, FACR
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Extrinsic Compression
Post-Traumatic Stenosis
Tracheobronchomalacia
Saber-Sheath Trachea
Less Common
Tracheobronchopathia Osteochondroplastica
Wegener Granulomatosis
Relapsing Polychondritis
Amyloidosis
Laryngeal Papillomatosis
Rare but Important
Tracheal Neoplasms
Rhinoscleroma
Complete Cartilaginous Rings
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Symptoms usually do not develop until tracheal lumen reduced > 50%
Even with fixed obstruction, symptoms often episodic, leading to misdiagnosis of asthma
Normal tracheal size
Males: Coronal 13-25 mm; sagittal 13-27 mm; mean 20 mm
Females: Coronal 10-21 mm; sagittal 10-23 mm; mean 16 mm
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Extrinsic Compression
Common etiology: Goiter, vascular rings, mediastinal fibrosis
Airway wall usually normal (except for mediastinal fibrosis)
Narrowing often concentric
May have secondary tracheomalacia
Post-Traumatic Stenosis
Common causes: Prolonged intubation, penetrating or blunt chest trauma, post-surgery
Intubation: Location either at tracheal stoma or level of tube balloon
Airway wall usually thickened
CT coronal reconstructions more sensitive than axial imaging
Tracheobronchomalacia
Defined as dynamic decrease in airway luminal diameter of > 70%
Crescent or lunate shape with ballooning of posterior tracheal membrane into airway lumen
May be primary or acquired
Confident diagnosis requires dynamic CT: Comparison of inspiratory and expiratory luminal diameters
Forced expiration or coughing more sensitive than tidal breathing
Saber-Sheath Trachea
Associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Narrow side-to-side diameter, anteroposterior diameter increased
Extrathoracic trachea normal
Airway wall thickness normal
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Tracheobronchopathia Osteochondroplastica
Nodular excrescences of cartilage spare posterior membrane and may be calcified
Size: 2-3 mm in diameter
Associated with elderly patients; usually incidental finding at autopsy
Wegener Granulomatosis
Systemic necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis
Typical is subglottic narrowing with thickening of airway wall; may be diffuse or focal
May have thick-walled cavitary lung lesions
Relapsing Polychondritis
Systemic autoimmune disorder with cartilage destruction
Airway involvement more common in women (M:F = 1:3); stenosis occurs late
Airway wall thickening either focal or diffuse and may have increased attenuation
Spares posterior tracheal membrane
Amyloidosis
Airway involvement most common form of pulmonary amyloidosis
Airway involvement most common in localized amyloidosis
Focal or diffuse nodular soft tissue thickening of airway wall ± calcification/ossification
Laryngeal Papillomatosis
Due to human papilloma virus
Younger patients
May seed lungs with solid to thin-walled cystic nodules
At risk to develop squamous cell carcinoma (2%)
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Tracheal Neoplasms
Rare tumors, 2/3 either squamous cell carcinoma or adenoid cystic carcinoma
More likely to have extraluminal extension and mediastinal adenopathy
Adenoid cystic carcinoma: Longitudinal extent > transaxial extent, and tumor usually more than 180° of airway circumference
Fat content suggests lipoma or hamartoma
Rhinoscleroma
a.k.a. Klebsiella rhinoscleromatis
Chronic granulomatous infection of upper respiratory tract
Endemic in Central America and Africa
Diffuse airway wall thickening, nasal polyps, enlarged turbinates, and thickening nasopharynx common
Complete Cartilaginous Rings
a.k.a. napkin rings
Associated with pulmonary artery sling
Complete rings may be diffuse or focal (most commonly distal trachea)
Alternative Differential Approaches
Focal narrowing
Extrinsic compression
Post-traumatic stenosis
Tracheal neoplasms
Subglottic narrowing
Post-intubation stenosis
Wegener granulomatosis
Rhinoscleroma
Sarcoidosis
Diffuse narrowing
Tracheomalacia
Saber-sheath trachea
Tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica
Relapsing polychondritis
Sparing posterior tracheal membrane
Relapsing polychondritis
Tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica
Normal wall thickness
Extrinsic compression
Tracheomalacia
Saber-sheath trachea
Complete cartilaginous rings
Tracheal wall calcification
Normal process of aging
Tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica
Amyloidosis
Relapsing polychondritis
Long-term warfarin therapy
Image Gallery
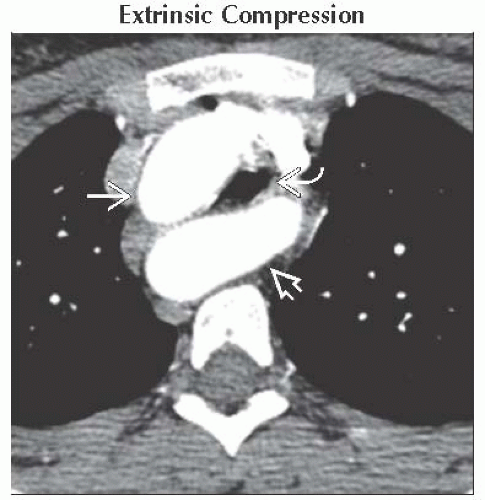 Axial CECT shows right cervical aortic arch
 and aberrant left subclavian artery and aberrant left subclavian artery  extrinsically compressing the trachea extrinsically compressing the trachea  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|