4 The Mitral Valve
Anatomic Components
Mitral Leaflets
The surface area of the two mitral leaflets is nearly the same, but their shape is very different.
The annular length of the posterior leaflet is about twice that of the anterior leaflet, but the height of the anterior leaflet is more than twice that of the posterior leaflet. The area of the leaflets is about 2.5 times the area of the mitral valve annulus. The leaflets are in continuity with each other, apposing over several millimeters, to achieve coaptation and competence and a reserve of coaptation.
Papillary Muscles
The Posteromedial Papillary Muscle
 The posteromedial papillary muscle usually is smaller, and often consists of multiple insertions into the left ventricle, and sometimes even of multiple separate trunks.
The posteromedial papillary muscle usually is smaller, and often consists of multiple insertions into the left ventricle, and sometimes even of multiple separate trunks.
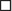 Most patients have either two “heads” or two adjacent “trunks” of the posteromedial papillary muscle.
Most patients have either two “heads” or two adjacent “trunks” of the posteromedial papillary muscle.
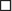 Rupture of the posteromedial papillary muscle has the chance of involving one head or trunk, leaving the other intact, and resulting in less fulminant MR than would complete rupture of both heads or trunks, or of a solitary (e.g., anterolateral) papillary muscle.
Rupture of the posteromedial papillary muscle has the chance of involving one head or trunk, leaving the other intact, and resulting in less fulminant MR than would complete rupture of both heads or trunks, or of a solitary (e.g., anterolateral) papillary muscle.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree