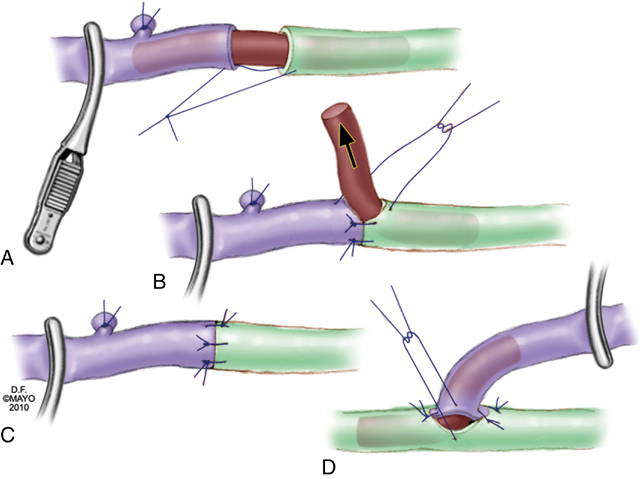
Microsurgical lymphovenous anastomoses in the leg are performed between lymph vessels of the superficial medial lymphatic bundle and usually with superficial veins. The most commonly performed techniques are direct end-to-end, end-to-side, or side-to-end microsurgical anastomoses using high-power magnification, supermicroscopic techniques, and fine 9–0 to 11–0 monofilament sutures. Important technical improvements include using 6–0 or 7–0 monofilament sutures to stent the lymph vessel or a small vein for easier and better anastomosis (Figures 1 and 2). The other is the side-to-end lymphovenous anastomosis technique that, in theory, can keep the lymph vessel patent even if the vein occludes after surgery. This might prevent progression of the lymphedema as a complication of surgical treatment.
Surgical Treatment of Lymphedema
Microsurgical Lymph Vessel Reconstructions
Lymphovenous Anastomoses
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Surgical Treatment of Lymphedema
