Figure 1.1 Frontal view.
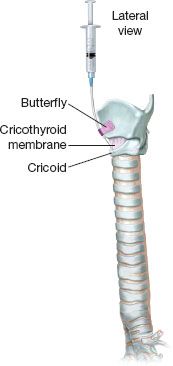
Figure 1.2 Lateral view.
Others prefer passing the flexible bronchoscope through the nose. Sometimes this is difficult due to abnormalities in anatomy or bleeding that may ensue. To prepare the patient for transnasal insertion, it is best to spray the nose with 1% or 2% Xylocaine; 4 cc is the amount used. Sometimes epinephrine should be included with this to constrict blood vessels and reduce the risk of bleeding. Cotton swabs soaked in Xylocaine can be placed into the nasal passage to aid in anesthetizing the area. Patients are still required to gargle with Xylocaine and spray the back of the throat as they will be sensitive when the scope enters the pharynx. The same procedure for the vocal cords, either using the butterfly technique or directly applying Xylocaine through the bronchoscope to the cords, is necessary.
The flexible bronchoscope has many other ways in which it can be effectively used. Passing it through the rigid bronchoscope allows careful inspection of the distal airway while still maintaining ventilation of the patient. Placing an uncuffed endotracheal tube over the flexible bronchoscope allows it to be inserted after proper topical anesthesia, control of the airway and repeatedly removing the bronchoscope as specimens are obtained (Fig. 1.3). The uncuffed or cuffed endotracheal tube can be connected to oxygen and supplement the patient’s oxygen in that fashion. A small adaptor can be connected to tubing with oxygen and the cap allows insertion of the bronchoscope. Another effective means of inserting the flexible bronchoscope is with a laryngeal mask airway that has been inserted at the beginning of anesthesia. With this same connecting tubing, the patient can be ventilated while working through the connector. It has been my experience that a little topical anesthesia is oftentimes effective in allowing the flexible bronchoscope to be inserted easily under the epiglottis and into the airway. Even though the patient may be deeply anesthetized, their cough reflex is somehow maintained. With patience and a little topical Xylocaine, this reflex is eliminated. In emergencies, a small endotracheal tube can be threaded over a bronchoscope, inserted through an laryngeal mask airway (LMA) and inserted into the airway. This may be useful in certain emergencies where control of the airway is difficult and/or the operator is inexperienced with other methods of controlling the airway.
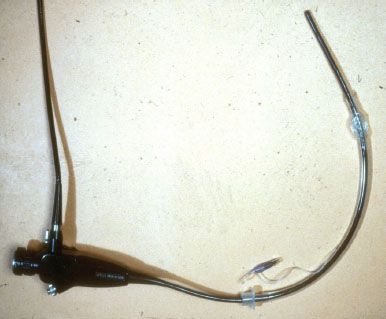
Figure 1.3 A well-lubricated endotracheal tube is threaded over an adult flexible bronchoscope.
In some cases, evaluating and controlling the airway is best done with a flexible bronchoscope with an endotracheal tube threaded over it (Figs. 1.1 and 1.2). This can be done under local anesthesia. This can be done as an awake intubation. It can be done when there is suspected trauma and concern exists about the status of the airway. The operating surgeon should choose a flexible bronchoscope that has adequate suctioning as oftentimes secretions or blood is a part of the problem. It should be well lubricated to pass easily through a no. 7 endotracheal tube although smaller sizes can be used depending upon the circumstances. Pediatric scopes can also be used; however, they provide little resistance to guide a tube into the airway and are inadequate for suctioning in most cases. Once the airway has been safely entered, the endotracheal tube can be advanced over the scope while continuously observing the airway through the bronchoscope to be certain it has not come out of the airway. It sometimes is required to have a little gentle jaw thrust to allow the endotracheal tube to pass easily. Once the airway is secured, suctioning and anesthesia can be done.
Once the flexible bronchoscope has been inserted, it can be used for many purposes. Its simplest use is to make careful observations, locate tumors, strictures, or the source of bleeding. If biopsies are required, bronchoscopic flexible forceps can be passed through the working channel and biopsies obtained under direct vision. Some foreign bodies can be removed with the biopsy forceps; however, a snare is sometimes more efficacious in trying to remove a foreign body with the flexible bronchoscope. Adult flexible bronchoscopes with an adequate channel can be used to pass balloon dilators and dilate strictures or tamponade areas of bleeding. Bronchoscopic washings and brushings can be performed through the flexible bronchoscope.
 COMPLICATIONS
COMPLICATIONS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


