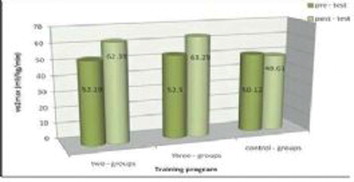
The present paper compares the effects of frequency and intensity of anaerobic exercises on legs explosive power and aerobic power of martial arts sportsmen. 45 martial arts sportsmen (aged 16-+ 1.93 on average and height average equal to 167-+0.09 centimeters and weighed 57.43+- 11.25 kilograms) were selected by questionnaire (from among 120 people) and were put into three 15-member groups (two exercise groups and one control group). Pretest and final test measurements involved legs explosive power and aerobic power. Respondents exercised 8 weeks in two exercise groups, one group took part in two session highly intense exercises and the other group took part in three-session moderate exercises. The control group did not have any regular and planned exercises during the eight weeks. The exercises included Plyometric, speed running and acceleration running which were conducted in different intensities in the two groups. These alternative exercises lasted 75 minutes in each session. The three-session group did moderately-intense exercises and the two-session group conducted highly-intense exercises and ANOVA analysis showed that changes in explosive power and aerobic power had significant differences in the two groups in comparison with the control group (p<= 0.05). However, there was no difference between the average and highly-intense exercise groups in the changes of the variables (p<=0.05). Results showed that highly-intense twosession exercises and moderately-intense three-session exercises had almost similar effects in many physical education factors like aerobic and anaerobic power.