Epidemic season 2013/2014
Influenza virus strains
A/H1N1/
A/H3N2/
B
A/California/7/2009 (H1N1)pdm09 – like virus
A/Victoria/361/2011 (H3N2) – like virus
B/Massachusetts/2/2012 – like virus
3 Results and Discussion
The geometric mean titers of anti-HA antibodies in sera collected from people in different age groups in the epidemic season 2013/2014 are shown in Fig. 1. The highest level of antibodies against hemagglutinin H1 was found in the age group 4–7 (GMT-27.51). The GMT of anti-H1 antibodies was slightly lower in the age group 8–14 (15.60) and low in the age groups 0–3, 15–25, 26–44 and 45–64, where there was almost the same level of antibodies (12.09-13.44). The lowest level of anti-H1 antibodies was observed in the age group ≥65 (GMT-10.05). In the case of the H3 hemagglutinin, the highest geometric mean titers were in the 4–7 (21.14) and 8–14 (20.37) years old groups. In other age groups, these values were at similar levels from 11.97 to 15.58. For type B hemagglutinin the observed level of antibodies was the highest in group of 15–25 years (GMT-24.85), lower in group of 8–14 years (GMT-12.14), and the lowest in groups of 0–3 and 4–7 years (GMT: 9.55 and 10.67, respectively). Almost identical geometric mean titers were observed in the age groups 26–44 (17.01), 45–64 (16.99), and ≥65 (16.17). In conclusion, the highest GMT titers were observed in the age groups: 4–7, 8–14, and 15–25, and a different type of anti-HA antibody had dominated in each of these groups: H1, H3 and B, respectively. The lowest geometric mean titer of antibody directed against the HA was observed in children aged 0–3 years.
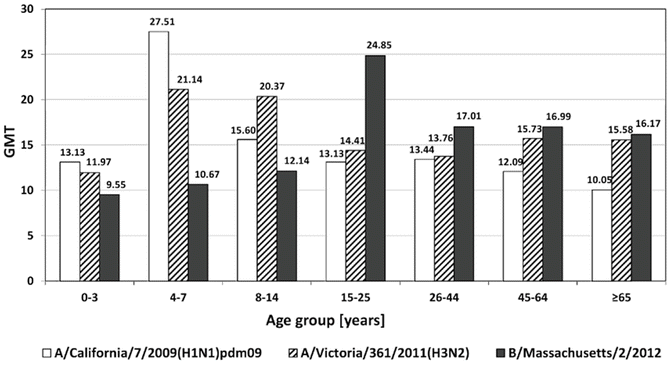

Fig. 1
Geometric mean titers of anti-HA antibodies in sera of people in different age groups in the epidemic season 2013/2014
The protection rate is the percentage of people with the protective titer of anti-HA antibodies of at least 40 after vaccination and, depending on age, should achieve different values: ≥70 % for people aged 18–60 years and ≥60 % for people over 60 years of age (Brydak 2008). However, the protection rate did not exceed 60 % in any age group (Fig. 2). The highest level of protection rate was observed for the hemagglutinin H1 of A/California/7/2009pdm09 strain in the age group 4–7 (53.33 %). An analysis of the protection rate with respect to the age group, including all three types of hemagglutinin, revealed that in the 0–3 years old group the level of protection exhibited similar values: 16.00 % (B), 20.67 % (H3), and 26.67 % (H1) without the domination of particular hemagglutinin type. In the age groups 4–7 and 8–14, the protection rate for H1 and H3 hemagglutinins was much higher than for hemagglutinin type B. However, in 15–25, 26–44 and 45–64 years old groups significantly higher protection rates were observed for type B hemagglutinin compared to the other two types.
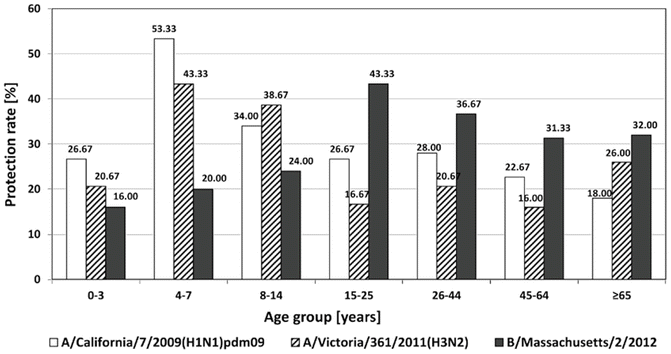

Fig. 2
The percentage of people with protective level of anti-HA antibodies with titers of at least 40 in the epidemic season 2013/2014
In the last three epidemic seasons: 2011/2012, 2012/2013 and 2013/2014, the values of protection rate were different in particular age groups (Table 2). The comparison of protection rates for hemagglutinin H1 of A/California/7/2009pdm09 strain is especially interesting. This type of A influenza virus has been circulating in the population since 2009. In the age groups of 4–7, 26–44, 45–64, and ≥65 years there has been a significant increase in the protection rate compared to the previous two seasons. In the youngest age group this value is higher in comparison to the last season, but lower than in the 2011/2012 season. However, in groups of 8–14 and 15–25 years old the protection rates remain at a similar level in all analyzed seasons. In the case of H3 hemagglutinin of A/Victoria/361/2011 strain the protection rate increased in the age group 4–7, decreased in the age group 26–44, and did not change significantly in the group of 8–14 years, compared to the previous two epidemiological seasons. There has been a significant increase in the values of this factor in groups 15–25, 45–64, and ≥65 years old as compared to the epidemic season 2012/2013. With regard to the last season, value of protection rate substantially increased in the youngest group. A significant increase in protection rates was observed in four age groups: 0–3, 4–7, 15–25, and 26–44 for influenza B virus strain B/Massachusetts/2/2012 in epidemic season 2013/2014. In other age groups these values were similar to 2011/2012 season and lower than in previous season.
Table 2




Protection rate values (%) in the epidemic seasons 2011/2012, 2012/2013 and 2013/2014 (Bednarska et al. 2014)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


