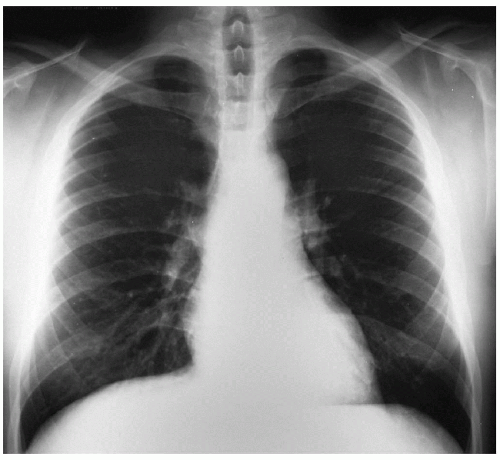
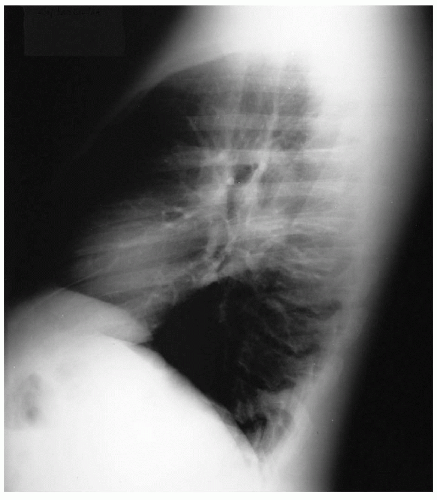
Leiomyoma
Presentation
A 36-year-old man is referred to your office by his primary medical doctor for evaluation of difficulty swallowing. He presents with the following chest x-rays.
Differential Diagnosis
In addressing symptoms of dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), the physician needs to conduct a thorough history to differentiate it from the symptoms of odynophagia (pain with swallowing) and globus (sensation of lump in the throat). Furthermore, symptoms of dysphagia can be divided into oropharyngeal dysphagia and esophageal dysphagia. Oropharyngeal dysphagia is the dysfunctional transfer of food bolus past the pharynx and upper esophageal sphincter and is more common in elderly patients, with stroke being the primary causative pathologic process. Esophageal dysphagia is caused by disordered peristaltic motility or conditions that obstruct flow of food or liquid bolus through the esophagus. Achalasia and scleroderma are the leading causes of esophageal motility disorders, with cancer, stricture, and Schatzki’s ring being the most common causes of esophageal obstruction.
Recommendation
A detailed history and physical examination are necessary to distinguish the symptoms of dysphagia from odynophagia and globus. A thorough physical examination, including a neurologic examination, is necessary.
Case Continued
The patient complains that food is sticking in his chest after swallowing. He denies any difficulty with swallowing and does not experience coughing during swallowing. He reports symptoms only with swallowing solids; liquids do not produce any symptoms. The patient states he is otherwise healthy and rarely ever takes medications except over-the-counter pain medications for occasional musculoskeletal aches after intense workouts. The patient denies any weight loss. His symptoms have progressed in the past 2 to 3 years. The patient states that he has been evaluated for these symptoms within the past week and that he did not follow up with his prior physicians because of his extreme discomfort during an esophagoscopy. He further reports that a biopsy was performed at that time and was normal.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree