Figure 22.2 Parasternal short-axis view shows the flat septum. LV, left ventricle; RV, right ventricle.
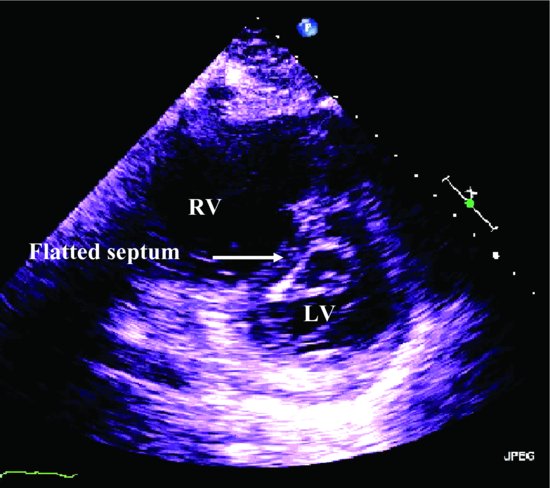
Moderate TR with an RV estimated pressure of 34 mmHg was seen (Videoclip 22.3). Dilated IVC, with respiratory size variation greater than 50%, consistent with elevated RA pressure was noted. Trivial pericardial effusion was present.
Discussion
The RV has the same cardiac output as the LV. It has one-sixth as much muscle mass and performs one-fourth the stroke work, because the pulmonary vascular resistance is one-tenth of the systemic resistance [1].
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


