Interstitial Pattern, Pleural Thickening and Effusion
Christopher M. Walker, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Pulmonary Edema
Less Common
Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis
Asbestosis
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rare but Important
Lymphangiomyomatosis
Diffuse Pulmonary Lymphangiomatosis
Pulmonary Venoocclusive Disease
Pulmonary Capillary Hemangiomatosis
Erdheim Chester Disease
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Chronicity of process and response to diuretics helps guide differential
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Pulmonary Edema
Caused by increased capillary hydrostatic pressure
New onset edema in outpatient without apparent cause may be secondary to myocardial infarction
Radiographic and CT findings
Cardiomegaly
Right ≥ left pleural effusions
Smooth interlobular septal thickening or Kerley B lines
Dependent lung distribution (posterior lung in supine patient and lower lung in upright patient)
± lobular or centrilobular ground-glass opacity with fissural thickening
Spared lobules among affected lobules secondary to differing lobular perfusion
Crazy-paving; intralobular interstitial thickening superimposed on ground-glass opacity
Mild lymph node enlargement secondary to increased lymphatic drainage
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis
Metastatic disease to lymphatics from
Breast, lung, stomach, colon, cervix, prostate, pancreas, and thyroid carcinoma among others
Smooth or nodular or “beaded” thickening of interlobular septa and peribronchovascular interstitium
Preserves underlying lung architecture
No change with diuretics
± hilar/mediastinal lymphadenopathy
± pleural effusions
Unilateral disease more common in lung carcinoma
Look for other sites of metastatic disease (liver or bone)
Asbestosis
Prone imaging important in diagnosis
HRCT findings
Posterior and basal subpleural lung
Subpleural reticular or dot-like opacities indicates early fibrosis
Subpleural lines parallel pleural surface
Short or long parenchymal bands extend inward from abnormal pleural surfaces
Pleural plaques
Late fibrosis shows honeycombing and thickening of interlobular septa
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Elevated antinuclear antibodies in young women
HRCT shows
Ground-glass and reticular opacities in a basal, posterior, and subpleural distribution
Traction bronchiectasis or bronchiolectasis
Pleural thickening or effusion seen in 50% of patients
± anterior upper lobe involvement
Honeycombing is rare
Ground-glass opacity
Represents lupus pneumonitis, pneumonia, or hemorrhage
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Lymphangiomyomatosis
Women of childbearing age
Large lungs with pleural effusions and associated pneumothoraces
Diffuse distribution of round lung cysts
± renal angiomyolipomas
± mediastinal and retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy
Diffuse Pulmonary Lymphangiomatosis
Congenital lymphatic disorder with proliferation and dilatation of lymphatics
Findings confined to thorax
Smooth thickening of interlobular septa and bronchovascular bundles
± pleural and pericardial effusions
Mediastinal lymphadenopathy with effacement of mediastinal fat
± centrilobular nodules
Pulmonary Venoocclusive Disease
Occlusion of small pulmonary veins and venules leading to pulmonary hypertension
Fatal pulmonary edema can follow standard vasodilator therapy
CT shows
Pulmonary arterial diameter ≥ 29 mm
± pleural effusions
Smooth or nodular interlobular septal thickening
Diffuse, geographic, perihilar or centrilobular ground-glass opacity
Pulmonary Capillary Hemangiomatosis
Proliferation of thin-walled capillaries leading to obstruction of pulmonary venules
Fatal pulmonary edema can follow standard vasodilator therapy
Overlap with imaging findings of venoocclusive disease
CT shows
Pulmonary arterial diameter ≥ 29 mm
Diffuse ill-defined centrilobular nodules of ground-glass opacity
± pleural effusions
Sparse interlobular septal thickening
Erdheim Chester Disease
Non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis
1/3 have pulmonary involvement
Visceral pleural thickening with effusions
Smooth interlobular septal and fissural thickening
Extrapulmonary findings
Symmetric osteosclerosis of metadiaphysis of long bones
± circumferential long segment aortic wall thickening
± soft tissue encasement of kidneys
± pericardial thickening
± nodular thickening of dura
± T2/FLAIR hyperintensity within brainstem
Image Gallery
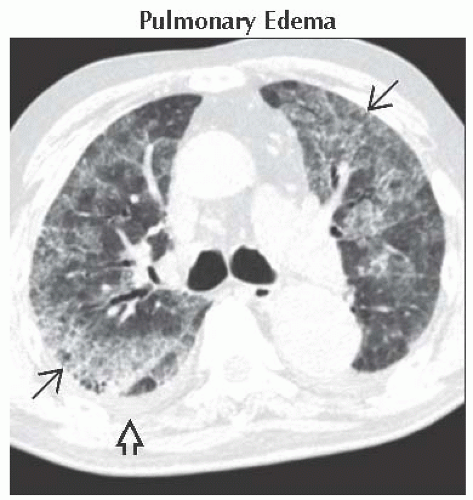 Axial HRCT shows a crazy-paving pattern, i.e., ground-glass opacities with intralobular interstitial thickening
 . Note pleural effusion . Note pleural effusion  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|