Halo Sign
Robert B. Carr, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Angioinvasive Aspergillosis
Less Common
Pulmonary Metastasis
Kaposi Sarcoma
Wegener Granulomatosis
Rare but Important
Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma
Atypical Infection
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Halo sign refers to ring of ground-glass opacity surrounding pulmonary mass or nodule on CT
Ground-glass opacity usually represents alveolar hemorrhage
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Angioinvasive Aspergillosis
Occurs in immunocompromised patients, especially AIDS, organ transplant, and chemotherapy
Fungal invasion with occlusion of small-and medium-sized pulmonary arteries
Results in tissue infarction, necrosis, and hemorrhage
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Pulmonary Metastasis
Central nodule represents metastatic lesion
Halo surrounding nodule represents hemorrhage
May be seen uncommonly with numerous malignancies, including melanoma, choriocarcinoma, and angiosarcoma
Kaposi Sarcoma
Usually occurs in patients with AIDS
Commonly preceded by appearance of mucocutaneous lesions
Ill-defined nodules in peribronchovascular distribution
Some nodules produce halo sign due to surrounding hemorrhage
Wegener Granulomatosis
Bilateral nodules and masses usually > 2 cm in size with no predilection for specific lung region
Approximately 50% of cases show cavitation
Look for associated tracheal involvement
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma
Lepidic growth: Growth along alveolar and bronchiolar walls and septa without stromal invasion
Halo sign is caused by infiltration of tumor cells growing in lepidic fashion
May have internal bubbly lucencies referred to as pseudocavitation
Atypical Infection
Has been described with tuberculosis, MAI, CMV, HSV, Mucor, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, pseudomonas
Image Gallery
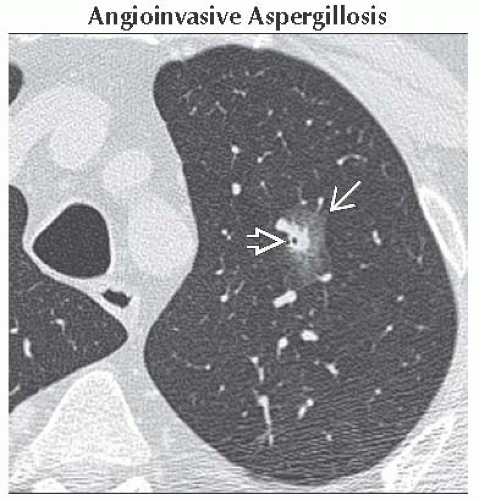 Axial NECT shows a pulmonary nodule in the left upper lobe
 , which is partially surrounded by a rim of ground-glass opacity , which is partially surrounded by a rim of ground-glass opacity  . This halo was caused by angioinvasive aspergillosis. . This halo was caused by angioinvasive aspergillosis.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|