Filling Defect, Pulmonary Artery
Jeffrey P. Kanne, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Pulmonary Emboli
Less Common
Tumor Embolism
Rare but Important
Abnormal Tubes and Catheters
Pulmonary Artery Sarcoma
Air Embolism
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Bland thrombi, tumor thrombi, and pulmonary artery sarcoma can have similar imaging appearances
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Pulmonary Emboli
Acute pulmonary thromboembolism
Complete or partial filling defect
Peripheral consolidation and ground-glass opacity from pulmonary hemorrhage or infarct
Residual thrombus in right heart
Right ventricular dilation from right heart strain (indicator of worse prognosis)
Chronic pulmonary thromboembolic disease
Eccentric clot contiguous with arterial wall
Uncommonly calcify
Webs and stenoses with post-stenotic dilation
Mosaic pattern of attenuation
Bronchial artery hypertrophy
Methylmethacrylate emboli
High-attenuation filling defect in pulmonary artery
Cement in spine from vertebroplasty
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Tumor Embolism
Renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and carcinoma of breast, stomach, and prostate most common
Filling defect in central pulmonary arteries
Tumor thrombus in inferior vena cava suggestive
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Abnormal Tubes and Catheters
Retained or embolized catheter
Pulmonary Artery Sarcoma
Vast majority arise in pulmonary valve or large pulmonary arteries
Large, lobulated, low-attenuation filling defect
Extension outside of vessel lumen
Enhancement on CT or MR or uptake on FDG PET/CT
Air Embolism
Frequently iatrogenic
Intravenous line placement or utilization
Barotrauma from positive-pressure ventilation
Scuba diving
Image Gallery
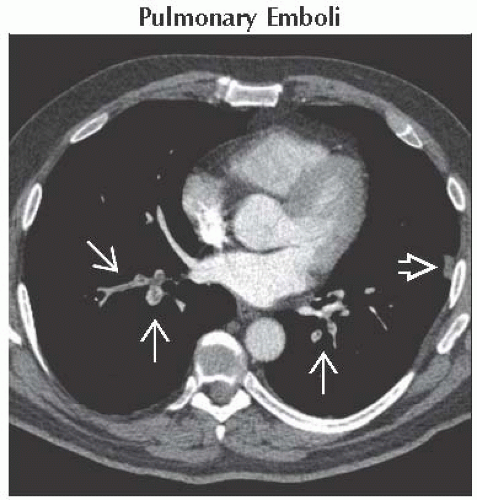 Axial CECT shows multiple acute pulmonary arterial filling defects
 . Note dilation of the affected arteries. Focal atelectasis, hemorrhage, or infarct is present in the left lower lobe . Note dilation of the affected arteries. Focal atelectasis, hemorrhage, or infarct is present in the left lower lobe  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|