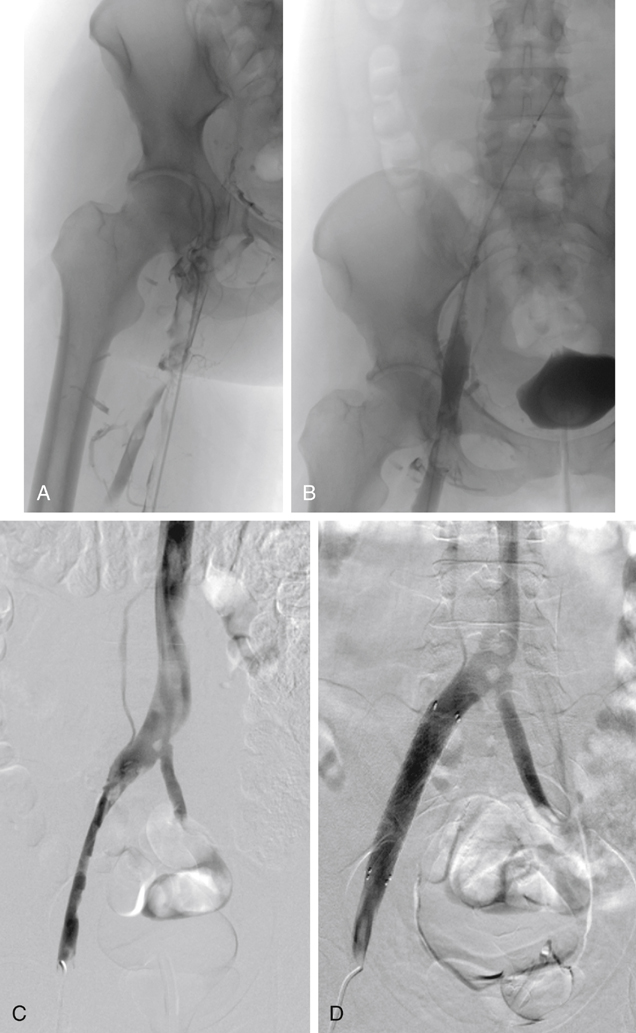
Complementing CDT with adjunctive mechanical methods is rapidly becoming the preferred method of catheter-based management of extensive DVT (Figure 1). Percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy alone is less successful than CDT and is associated with prolonged thrombolytic infusion times, prolonged intensive care unit stay, higher drug costs, and greater risks of hemorrhagic complications. Preliminary observations suggest that combining mechanical techniques with lytic infusion (pharmacomechanical thrombolysis, or PMT) results in a more effective lytic response in a shorter time.
Endovascular Thrombolysis and Mechanical Clot Removal for Acute Symptomatic Lower Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis
Endovascular Strategies of Thrombus Removal
Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis
Pharmacomechanical Thrombolysis
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Endovascular Thrombolysis and Mechanical Clot Removal for Acute Symptomatic Lower Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis
