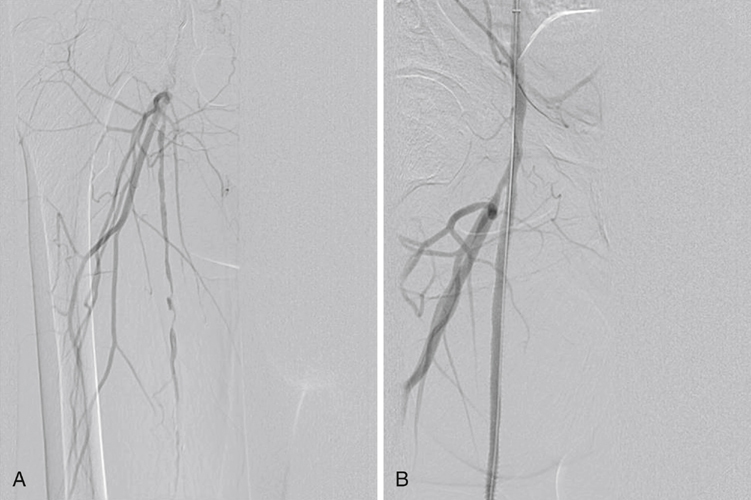
It is not clear at present which lesions are best treated with covered stents versus bare-metal self-expanding nitinol stents or ultimately surgical bypass (Table 1). Many interventionists use covered stents for Trans-Atlantic Inter-Society Consensus (TASC) C (>15 cm long) and D (>20 cm long) lesions of the superficial femoral artery (Figure 1). The most commonly used and only U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved stent for this indication is the Viabahn graft (Gore, Flagstaff, AZ). This is a nitinol stent surrounded by expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) that can also include a heparin lining. Viabahn is also used in the popliteal artery; it needs to be carefully sized because this artery often tapers somewhat as it descends. There is a greater likelihood of covering important perigenicular collaterals when the stent is deployed in the popliteal artery. There is no correctly sized self-expanding stent graft for the tibial arteries. The Symphony covered stent is a self-expanding covered nitinol stent with more radial force than the Viabahn. Use of this device in the lower extremity is off label. TABLE 1 Comparison of Endovascular Grafts, Standard Stents, and Femoral–Popliteal Bypass General technical points include appropriate access sheath sizing, aggressive predilatation, careful stent-graft sizing to the vessel within the instructions for use (Table 2), understanding the directionality of the deployment system, attention to full expansion at the ends of the graft, and avoidance of unnecessary coverage of collateral arteries. TABLE 2 Instructions for Sizing Viabahn Grafts∗
Endovascular Grafts in the Treatment of Lower Extremity Occlusive Disease
Indications
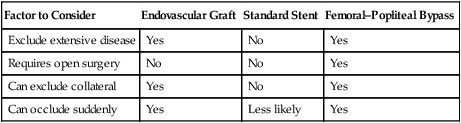
Factor to Consider
Endovascular Graft
Standard Stent
Femoral–Popliteal Bypass
Exclude extensive disease
Yes
No
Yes
Requires open surgery
No
No
Yes
Can exclude collateral
Yes
No
Yes
Can occlude suddenly
Yes
Less likely
Yes
Technique
Graft Size (mm)
Vessel Diameter (mm)
Device Profile (Fr)
5
4.0–4.7
7
6
4.8–5.5
7
7
5.6–6.5
8
8
6.6–7.5
8
9
7.6–8.5
9
10
8.6–9.5
11
11
9.6–10.5
11
13
10.6–12.0
12
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Thoracic Key
Fastest Thoracic Insight Engine