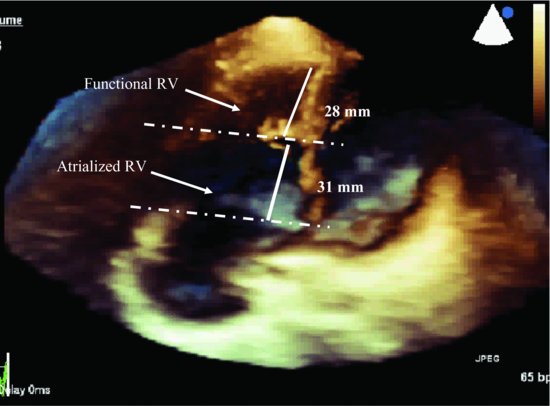
Figure 37.2 Apical 4-chamber view (three-dimensional) shows a small function right ventricle; the ratio of atrialized and functional right ventricle is 1:1. RV, right ventricle.
Eletrocardiogram demonstrated sinus rhythm, a short PR period and a delta wave suggesting pre-excitation of the Wolff-Parkinson-White-type A.
Electrophysiologic study revealed normal sinus node function and evidence of pre-excitation with a morphology suggesting a posterior right free wall pathway.
Discussion
Ebstein’s anomaly is a congenital heart disease in which the tricuspid valve is abnormally formed and it was first described by Wilhelm Ebstein in 1866. It occurs approximately 1 in 20,000 live births [1]. In Ebstein anomaly, the septal and/or posterior tricuspid valve leaflets are displaced apically into right ventricle (RV), and the anterior leaflet is elongated and may be adherent to the wall of the chamber. This leads to atrialization of RV with a variable degree of malformation and displacement of the anterior leaflet.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


