The spectral Doppler recording from the unusual flow demonstrates a continuous flow during cardiac cycle, which suggests this is a coronary artery fistula into RV (Figure 23.2).
Figure 23.2 Spectral Doppler recording from the unusual flow demonstrates a continuous flow during cardiac cycle, which suggests this is a coronary artery fistula into right ventricle.
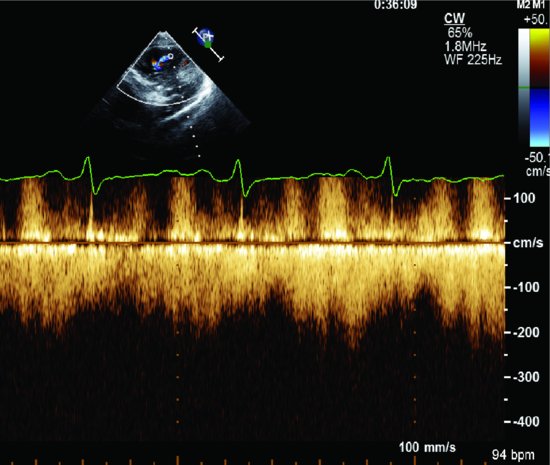
The color flows presented in diastole and systole suggest they are coronary artery fistulas into RV in both cases.
Discussion
Coronary artery fistula (CAF) accounts for 0.2–0.4% of congenital cardiac anomalies. Approximately 50% of pediatric coronary vasculature anomalies are CAFs [1]. Most CAF are congenital and may be found in patients with structurally normal hearts. Rarely, acquired forms of CAF may occur as a result of septal myectomy in association with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, muscle bundle resection in operative repair of tetralogy of Fallot, as a complication of radiofrequency ablation of accessory pathways, penetrating or nonpenetrating trauma, endomyocardial biopsy, permanent pacemaker implantation, or as a complication of coronary arterial procedures [2]. A CAF involves a sizable communication between a coronary artery, bypasses the myocardial capillary bed, and enters either a chamber of the heart (coronary-cameral fistula) or any segment of the systemic or pulmonary circulation (coronary arteriovenous fistula). CAF can affect persons of any age. But Liberthson et al
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


