12 Coronary Artery Disease
Stress Echocardiography
Stress Echocardiographic Images
Stress echocardiographic images may be used for the detection and determination of the following:
Wall Thickening/Ejection Fraction Response
Most wall thickening is a function of subendocardial thickening; only a minority of thickening is conferred by mid-wall and subepicardial systolic function. Partial occlusion of perfusing arteries leads to a fall by about half of subendocardial and overall wall thickening. Complete occlusion results in mild systolic wall thinning. Subendocardial blood flow is affected the most by a reduction in epicardial blood flow. Infarct thickness of only 30% results in a loss of systolic thickening.4
The normal ejection fraction response to exercise is an increase of almost 10%. Overall, in CAD there is a loss of exercise-induced increase in ejection fraction, the extent of which is determined by the extent of CAD:1
Available forms of Stress
Exercise stress echocardiography (physical stress)
 Treadmill exercise stress test
Treadmill exercise stress test
Stress echocardiography (pharmacologic stress) using incremental infusions of the following:
Stress echocardiography (pacing stress) does not raise blood pressure.
 Acquisition of images must be performed promptly at each level or step, and be performed quickly. Respiratory artifact becomes very prominent at higher levels of physical work, but all of the images are recorded so that after the study one complete, well-visualized cardiac cycle is selected and used for interpretation.
Acquisition of images must be performed promptly at each level or step, and be performed quickly. Respiratory artifact becomes very prominent at higher levels of physical work, but all of the images are recorded so that after the study one complete, well-visualized cardiac cycle is selected and used for interpretation.
Exercise Stress Echocardiography
Stress echocardiography is better at detecting multivessel disease than single-vessel disease:
Exercise stress echocardiography has been validated for female patients. The study included 161 female patients with no history of Q-wave infraction5:
| Exercise stress ECG | Exercise ECG | |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 81% | 77% |
| Specificity | 81% | 56% |
Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography
Dobutamine is delivered by graded infusion:
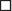 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 40, (±50) μg/kg/min
5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 40, (±50) μg/kg/min
 Atropine may or may not be given if there is no response at highest dose.
Atropine may or may not be given if there is no response at highest dose.
Safety and Tolerability6
Out of 2949 dobutamine tests, 341 were not completed because of side effects.
Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography for the Detection of Coronary Artery Disease
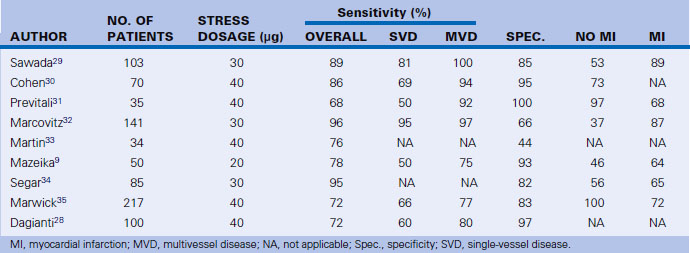
See Table 12-2 for a summary of different studies on the detection of CAD by stress echocardiography.
Dobutamine Stress Echocardiographyfor Perioperative Risk Assessment7
 Dipyridamole thallium-201: 10 reports, 1994 patients
Dipyridamole thallium-201: 10 reports, 1994 patients
 Dobutamine stress echocardiography: 5 reports, 445 patients
Dobutamine stress echocardiography: 5 reports, 445 patients
 Odds ratios for death or myocardial infarction (MI) and secondary end-points as predicted by dipyrdamole thallium versus stress echocardiography
Odds ratios for death or myocardial infarction (MI) and secondary end-points as predicted by dipyrdamole thallium versus stress echocardiography
A total of 367 patients were followed for 19 ± 11 months8:
| Relative risk | |
|---|---|
| Extensive wall motion abnormalities (WMA) (>3 segments) | 6.5-fold |
| Limited WMA (1–2 segments) | 2.9-fold |
| Prior MI | 3.8-fold |
| Extensive WMA + prior MI | 31-fold |
Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography for the Prediction of Reversible Myocardial Dysfunction Post–Myocardial Infarction
See Table 12-3 for a summary of this condition.
Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography for Post-Infarction Risk Assessment
 Using symptom-limited supine bicycle exercise stress echocardiography, 178 patients were studied.
Using symptom-limited supine bicycle exercise stress echocardiography, 178 patients were studied.
 Cumulative end-points of death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and unstable angina were recorded.
Cumulative end-points of death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and unstable angina were recorded.
| Dobutamine Echo Positive | ECG Positive | |
|---|---|---|
| Negative predictive value | 88% | 86% |
| Relative risk | 5.15 | Not significant |
Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography Validated to Detect Myocardial Hibernation
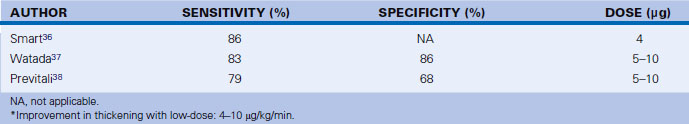
The response that best predicts hibernation is the biphasic response of inotropy at low-dose dobutamine, and ischemia at high-dose dobutamine. This is consistent with hibernation and inducible ischemia (Fig. 12-1).
| Rr Spect Thallium 201 | Low-Dose Dobutamine | |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (%) | 72 | 88 |
| Specificity (%) | 73 | 77 |
Ejection fraction improvement post-revascularization is approximately 1:1 with (i.e., 1% per) myocardial segments that demonstrate contractile reserve.11
Adenosine and Dipyridamole Stress Echocardiography
Dipyridamole stress echocardiography is superior (87% vs. 74%) to exercise electrocardiography in excluding CAD events over 5 years in evaluation of patients with suspected CAD.12
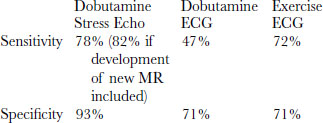
Comparison of Exercise, Dobutamine, and Dipyridamole Stress Echocardiography
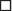
Only a few studies have directly compared different modalities/techniques of stress echocardiography (Table 12-6).
Transesophageal Stress Echocardiography
Transesophageal echocardiography would not be an initial form of stress imaging, but may be viewed as an alternative to stress echocardiography in patients with inadequate transthoracic images, and those who are unable to undergo stress MRI or nuclear procedures. Some patients in the intensive care unit may fall into this subset. Transesophageal stress echocardiography is validated13 using the transgastric short- and long-axis views.
Limitations of Stress Echocardiography
BOX 12-1 Stress Testing: Noninvasive Risk Stratification
High Risk (>3% Annual Mortality Rate)
 Severe resting LV dysfunction (LVEF < 35%)
Severe resting LV dysfunction (LVEF < 35%)
 High-risk treadmill score (score ≤ –11)
High-risk treadmill score (score ≤ –11)
 Severe exercise LV dysfunction (exercise LVEF < 35%)
Severe exercise LV dysfunction (exercise LVEF < 35%)
 Stress-induced large perfusion defect (particularly if anterior)
Stress-induced large perfusion defect (particularly if anterior)
 Stress-induced multiple perfusion defects of moderate size
Stress-induced multiple perfusion defects of moderate size
 Large, fixed perfusion defect with LV dilation or increased lung uptake (thallium-201)
Large, fixed perfusion defect with LV dilation or increased lung uptake (thallium-201)
 Stress-induced moderate perfusion defect with LV dilation or increased lung uptake (thallium-201)
Stress-induced moderate perfusion defect with LV dilation or increased lung uptake (thallium-201)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree