Cardiac Calcifications
Gregory Kicska, MD, PhD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Coronary Artery
Mitral Valve
Aortic Valve
Less Common
Pericardial
Myocardial
Other Cardiac Valves and Chambers
Rare but Important
Mass
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Most common pitfall is misidentifying which anatomic structure is calcified
Cardiac calcifications more common in dialysis patients
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Coronary Artery
Curvilinear, parallel lines most commonly in proximal coronary arteries and at vessel branch points
Amount of calcium correlates with amount of coronary plaque but not degree of stenosis
Presence correlates with risk of future cardiac events
Mitral Valve
Annular calcifications: Associated with mitral valve insufficiency
Valvular calcifications: Suggests stenosis, most often due to rheumatic heart disease
Aortic Valve
Calcification burden correlates with stenosis severity
Bicuspid valve: Young patient, coexistent coarctation
Degenerative: > 60 years old, risk factor for coronary atherosclerosis
Rheumatic heart disease: Coexistent mitral valve stenosis, > 35 years old
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Pericardial
Associated with constrictive pericarditis
Myocardial
Indicates prior infarction; myocardial fat will likely be present
Other Cardiac Valves and Chambers
Tricuspid valve: Most commonly due to rheumatic heart disease, mitral and aortic valve will likely be calcified
Pulmonary valve: Most commonly due to congenital pulmonary stenosis
Atrial calcifications: Associated with severe atrial dilation
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Mass
Chronic thrombus: Atrial appendage or adjacent to infarcted myocardium
Metastasis: History of primary tumor
Atrial myxoma: Look for characteristic location and attachment
Image Gallery
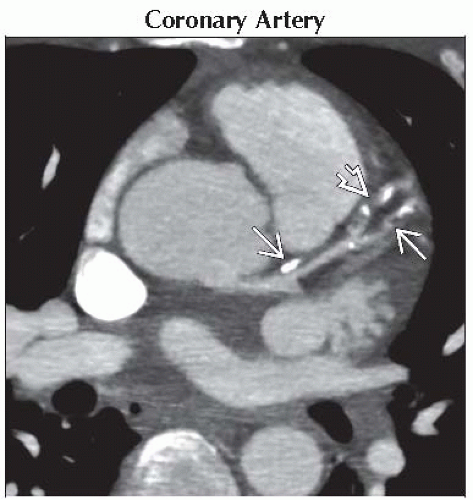 Axial oblique enhanced CT MIP shows discrete calcifications in a linear arrangement
 in a patient with LAD atherosclerosis. Note the presence of noncalcified plaque in a patient with LAD atherosclerosis. Note the presence of noncalcified plaque 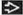 . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|