Chapter 21 Burns
More than 500,000 burn injuries occur annually in the United States.1 Although most of these burn injuries are minor, approximately 40,000 to 60,000 burn patients require admission to a hospital or major burn center for appropriate treatment. The devastating consequences of burns have been recognized by the medical community and significant amounts of resources and research have successfully improved these dismal statistics.2 Specialized burn centers (Box 21-1) and advances in therapy strategies, based on improved understanding of resuscitation, enhanced wound coverage, more appropriate infection control, improved treatment of inhalation injury, and better support of the hypermetabolic response to injury have further improved the clinical outcome of this unique patient population.3 However, severe burns remain a devastating injury, affecting almost every organ system and leading to significant morbidity and mortality.4,5
BOX 21-1 Burn Unit Organization and Personnel
Experienced burn surgeons (burn unit director and qualified surgeons)
Physical and occupational therapists
Psychiatrists and clinical psychologists
Causes
There is no greater trauma than a major burn injury, which can be classified according to different burn causes and different depths (Box 21-2). Of all cases, almost 4000 people die of complications related to thermal injury.6 As in all trauma-related deaths, burn deaths generally occur immediately after the injury or weeks later as a result of multisystem organ failure. Of all burns, 66% occur at home and fatalities are predominant in the extremes of age, the very young and older adults. The most common causes are flame and scald burns.7 Scald burns are most common in victims up to 5 years of age. There is a significant percentage of burns in children that are caused by child abuse. There are a number of risk factors that have been linked to burn injury—specifically age, location, demographics, and low economic status.8 These risk factors underscore the fact that most burn injuries and fatalities are preventable and mandate intervention and prevention strategies. Overall, no single group is immune to the public health debt caused by burns.
BOX 21-2 Burn Classifications
Causes
Flame—damage from superheated oxidized air
Scald—damage from contact with hot liquids
Contact—damage from contact with hot or cold solid materials
Chemicals—contact with noxious chemicals
Electricity—conduction of electrical current through tissues
Depths
First degree—injury localized to the epidermis
Superficial second degree—injury to the epidermis and superficial dermis
Deep second degree—injury through the epidermis and deep into the dermis
Third degree—full-thickness injury through the epidermis and dermis into subcutaneous fat
Fourth degree—injury through the skin and subcutaneous fat into underlying muscle or bone
Location plays a major role in the risk and treatment of burn. The available resources in a given community greatly influence morbidity and mortality. A lack of adequate resources affects the education, rehabilitation, and survival rates of burn victims. Someone with a severe burn in a resource-rich environment can receive care within minutes, whereas a burned individual in an austere environment may suffer for an extended period waiting for care. The ideal treatment of burns requires the collaboration of surgeons, anesthesiologists, occupational therapists, physiotherapists, nurses, nutritionists, rehabilitation therapists, and social workers just to accommodate the basic needs of a major burn survivor.9 Any delay in reaching these resources compounds a delay in resuscitation and thus adds to the mortality risk.10 For those who have access to adequate burn care, survival from a major burn is the rule, no longer the exception. The survival rate for all burns is 94.6%, but for at-risk populations, in communities lacking medical, legal, and public health resources, survival can be almost impossible.7
Pathophysiology of Burn Injuries
Local Changes
Locally, thermal injury causes coagulative necrosis of the epidermis and underlying tissues, with the depth of injury dependent on the temperature to which the skin is exposed, the specific heat of the causative agent, and the duration of exposure. Burns are classified into five different categories of cause and depth of injury. The causes include injury from flame (fire), hot liquids (scald), contact with hot or cold objects, chemical exposure, and/or conduction of electricity (Box 21-2). The first three induce cellular damage by the transfer of energy, which induces coagulation necrosis. Chemical burns and electrical burns cause direct injury to cellular membranes in addition to the transfer of heat and can cause a coagulation or colliquation necrosis.
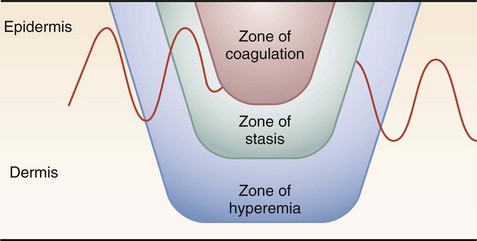
The skin, which is the largest organ on the human body, provides a staunch barrier in the transfer of energy to deeper tissues, thus confining much of the injury to this layer. Once the inciting focus is removed, however, the response of local tissues can lead to injury in the deeper layers. The area of cutaneous or superficial injury has been divided into three zones—zone of coagulation, zone of stasis, and zone of hyperemia (Fig. 21-1). The necrotic area of burn where cells have been disrupted is termed the zone of coagulation. This tissue is irreversibly damaged at the time of injury. The area immediately surrounding the necrotic zone has a moderate degree of insult, with decreased tissue perfusion. This is termed the zone of stasis and, depending on the wound environment, can survive or go on to coagulative necrosis. The zone of stasis is associated with vascular damage and vessel leakage. Thromboxane A2, a potent vasoconstrictor, is present in high concentrations in burn wounds, and the local application of inhibitors improves blood flow and decreases the zone of stasis. Antioxidants, bradykinin antagonists, and subatmospheric wound pressures also improve blood flow and affect the depth of injury. Local endothelial interactions with neutrophils mediate some of the local inflammatory responses associated with the zone of stasis. Treatment directed at the control of local inflammation immediately after injury may spare the zone of stasis, indicated by studies demonstrating the blockage of leukocyte adherence with anti-CD18 or anti-intercellular adhesion molecules; monoclonal antibodies improve tissue perfusion and tissue survival in animal models. The last area is termed the zone of hyperemia, which is characterized by vasodilation from inflammation surrounding the burn wound. This region contains the clearly viable tissue from which the healing process begins and is generally not at risk for further necrosis.
Burn Depth
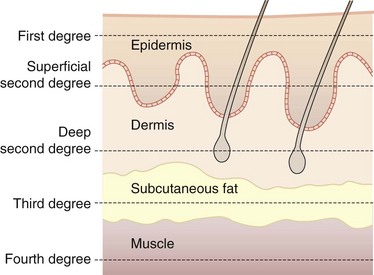
The depth of burn varies, depending on the degree of tissue damage. Burn depth is classified into degree of injury in the epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous fat, and underlying structures (Fig. 21-2). First-degree burns are, by definition, injuries confined to the epidermis. First-degree burns are painful, erythematous, and blanch to the touch, with an intact epidermal barrier. Examples include sunburn or a minor scald from a kitchen accident. These burns do not result in scarring, and treatment is aimed at comfort with the use of topical soothing salves, with or without aloe, and oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Fourth-degree burns involve other organs beneath the skin, such as muscle, bone, and brain.
Burn Size
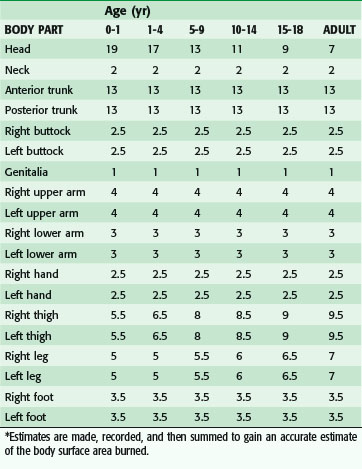
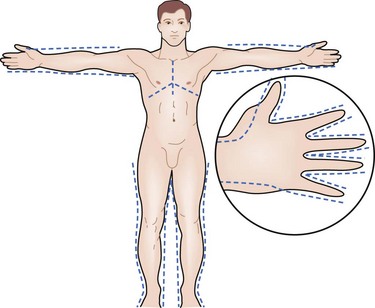
Determination of burn size estimates the extent of injury. Burn size is generally assessed by the rule of nines (Fig. 21-3). In adults, each upper extremity and the head and neck are 9% of the total body surface area (TBSA), the lower extremities and the anterior and posterior trunk are 18% each, and the perineum and genitalia are assumed to be 1% of the TBSA. Another method of estimating smaller burns is to equate the area of the open hand (including the palm and extended fingers) of the patient to be approximately 1% of the TBSA and then to transpose that measurement visually onto the wound for a determination of its size. This method is crucial when evaluating burns of mixed distribution.
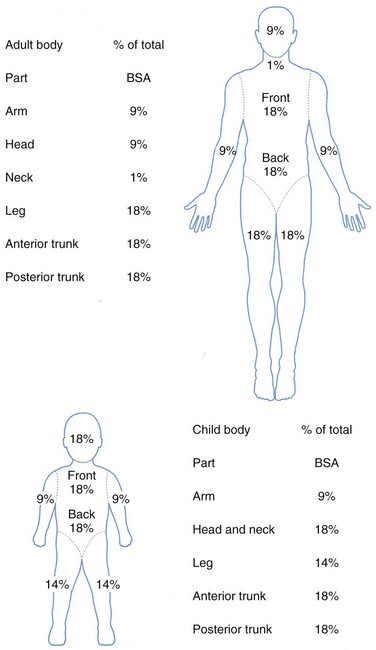
FIGURE 21-3 Estimation of burn size using the rule of nines.
(From American Burn Association: Advanced burn life support providers manual, Chicago, 2005, American Burn Association.)
Children have a relatively larger portion of the body surface area in the head and neck, which is compensated for by a relatively smaller surface area in the lower extremities. Infants have 21% of the TBSA in the head and neck and 13% in each leg, which incrementally approaches the adult proportions with increasing age. The Berkow formula is used to determine burn size accurately in children (Table 21-1).
Systemic Changes
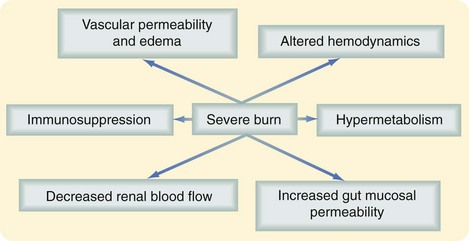
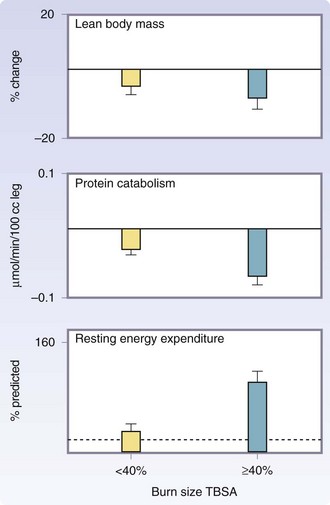
Severe burns covering more than 40% of the TBSA are typically followed by a period of stress, inflammation, and hypermetabolism, characterized by a hyperdynamic circulatory response with increased body temperature, glycolysis, proteolysis, lipolysis, and futile substrate cycling (Fig. 21-4). These responses are present in all trauma, surgical, and critically ill patients, but their severity, length, and magnitude are unique for burn patients.4
Hypermetabolic Response to Burn Injury
Marked and sustained increases in catecholamine, glucocorticoid, glucagon, and dopamine secretion are thought to initiate the cascade of events leading to the acute hypermetabolic response, with its ensuing catabolic state.11 The cause of this complex response is not well understood. However, interleukin-1 (IL-1) and IL-6, platelet-activating factor, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), endotoxins, neutrophil-adherence complexes, reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide, coagulation, and complement cascades have also been implicated in regulating this response to burn injury.12 Once these cascades are initiated, their mediators and byproducts appear to stimulate the persistent and increased metabolic rate associated with altered glucose metabolism seen after severe burn injury.
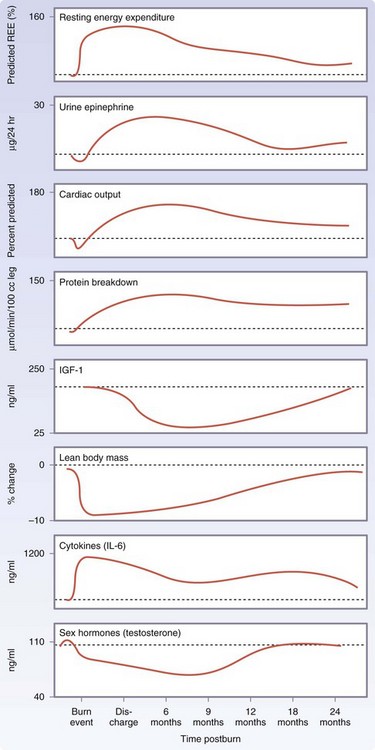
The postburn metabolic phenomena occur in a timely manner, suggesting two distinct patterns of metabolic regulation following injury. The first phase occurs within the first 48 hours of injury and has been called the ebb phase, characterized by decreases in cardiac output, oxygen consumption, and metabolic rate, as well as impaired glucose tolerance associated with its hyperglycemic state. These metabolic variables gradually increase within the first 5 days postinjury to a plateau phase (the flow phase), characteristically associated with hyperdynamic circulation and the hypermetabolic state.11,13 Insulin release during this period was found to be twice that of controls in response to glucose load and plasma glucose levels are markedly elevated, indicating the development of an insulin resistance.14 It is currently thought that these metabolic alterations resolve soon after complete wound closure. We have found that the hypermetabolic response to burn injury may last for more than 12 months after the initial event; in our recent studies,15 we noted that sustained hypermetabolic postburn alterations, as shown by persistent elevations of total urine cortisol, serum cytokine, and catecholamine levels, and basal energy requirements, were accompanied by impaired glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity that persisted for up to 3 years after the initial burn injury.
A 10- to 50-fold elevation of plasma catecholamine and corticosteroid levels occurs in major burns, which persist up to 3 years post-injury.4,13,15 Cytokine levels peak immediately after the burn injury, approaching normal levels only after 1-month postinjury. Constitutive and acute-phase proteins are altered beginning 5 to 7 days postburn and remain abnormal throughout the acute hospital stay. Serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), IGF-binding protein 3 (IGFBP3), parathyroid hormone, and osteocalcin levels decrease immediately after the injury 10 fold, and remain significantly decreased up to 6 months postburn compared with normal levels. Sex hormone and endogenous growth hormone levels decrease at approximately 3 weeks postburn (Fig. 21-5).
For severely burned patients, the resting metabolic rate at a thermal neutral temperature (30° C) exceeds 140% of normal at admission, reduces to 130% once the wounds are fully healed, and then to 120% at 6 months after injury and 110% at 12 months postburn.13 Increases in catabolism result in loss of total body protein, decreased immune defenses, and decreased wound healing.4
Immediate postburn patients have low cardiac output characteristic of early shock. However, 3 to 4 days postburn, the cardiac output is more than 1.5 times that of a nonburned healthy volunteer.13 Heart rates of pediatric burn patients approach 1.6 times those of nonburned, healthy volunteers.11 Postburn patients have increased cardiac work.4 Myocardial oxygen consumption surpasses that of marathon runners and is sustained well into the rehabilitative period.
There is profound hepatomegaly after injury. The liver increases its size by 225% of normal by 2 weeks postburn and remains enlarged at discharge at 200% of normal.13
Postburn, muscle protein is degraded much faster than it is synthesized.16 The net protein loss causes loss of lean body mass and severe muscle wasting, leading to decreased strength and failure to rehabilitate fully. Significant decreases in lean body mass related to chronic illness or hypermetabolism can have dire consequences. A 10% loss of lean body mass is associated with immune dysfunction. A 20% loss of lean body mass positively correlates with decreased wound healing. A loss of 30% of lean body mass leads to increased risk for pneumonia and pressure sores. A 40% loss of lean body mass can lead to death. Uncomplicated severely burned patients can lose up to 25% of total body mass after acute burn injury.13 Protein degradation persists up to almost 1 year after severe burn injury, resulting in significant negative whole-body and cross-leg nitrogen balance (Fig. 21-6).4 Protein catabolism has a positive correlation with increases in metabolic rates. Severely burned patients have a daily nitrogen loss of 20 to 25 g/m2 of burned skin.4 At this rate, a lethal cachexia can be reached in less than 1 month. Burned pediatric patients’ protein loss leads to significant growth retardation for up to 24 months postinjury.15
Elevated circulating levels of catecholamines, glucagon, and cortisol after severe thermal injury stimulate free fatty acids and glycerol from fat, glucose production by the liver, and amino acids from muscle (Fig. 21-7).4,11 Specifically, glycolytic-gluconeogenic cycling is increased 250% during the postburn hypermetabolic response, coupled with an increase of 450% in triglyceride fatty acid cycling. These changes lead to hyperglycemia and impaired insulin sensitivity related to postreceptor insulin resistance, as demonstrated by elevated levels of insulin and fasting glucose, and significant reductions in glucose clearance. Whereas glucose delivery to peripheral tissues is increased up to threefold, glucose oxidation is restricted. Increased glucose production is directed, in part, to the burn wound to support the relatively inefficient anaerobic metabolism of fibroblasts and endothelial and inflammatory cells. The end product of anaerobic glucose oxidation, lactate, is recycled to the liver to produce more glucose via gluconeogenic pathways. Serum glucose and insulin levels increase postburn and remain significantly increased through the acute hospital stay. Insulin resistance appears during the first week postburn and persists significantly after discharge, up to 3 years postburn.13,15
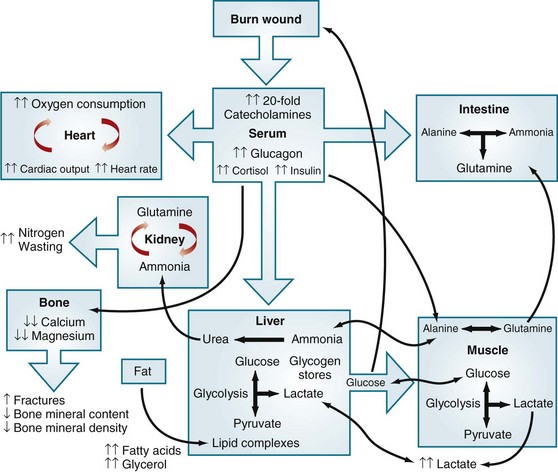
FIGURE 21-7 Effects of metabolic dysfunction postburn.
(From Williams FN, Jeschke MG, Chinkes DL, et al: Modulation of the hypermetabolic response to trauma: Temperature, nutrition, and drugs. J Am Coll Surg 208:489–502, 2009.)
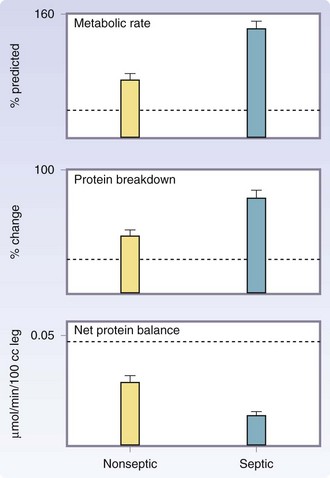
Septic patients have a profound increase in metabolic rates and protein catabolism, up to 40% more compared with those with burns of a similar size who do not develop sepsis.17,18 A vicious cycle develops, because catabolic patients are more susceptible to sepsis caused by changes in immune function and immune response. The emergence of multidrug resistant organisms has led to increases in sepsis, catabolism, and mortality (Fig. 21-8). Modulation of the hypermetabolic hypercatabolic response, thus preventing secondary injury, is paramount for the restoration of structure and function of severely burned patients.
Effects on the Cardiovascular System
Microvascular changes induce cardiopulmonary alterations characterized by loss of plasma volume, increased peripheral vascular resistance, and subsequent decreased cardiac output immediately after injury. Cardiac output remains depressed because of decreased blood volume and increased blood viscosity, as well as decreased cardiac contractility. Ventricular dysfunction during this period is attributed to a circulating myocardial depressant factor present in lymphatic fluid, although the specific factor has never been isolated. Burn patients with burns over 40% of their TBSA demonstrate an increased cardiac output, which significantly decreases over time. This is accompanied by an increase in heart rate. Severely burned pediatric patients have a marked tachycardia, with 160% to 170% predicted, which remains high at intensive care unit (ICU) discharge at (≈150%). Cardiac output at admission is 150% and remains high at discharge (≈130% predicted). There is some evidence that the heart rate remains elevated up to 2 years postburn.13 Increased cardiac stress postburn is associated with myocardial depression. which has been shown in several studies.19 The hypothesis that cardiac stress and myocardial dysfunction may be one of the main contributors to mortality in large burns was confirmed in a retrospective autopsy study, indicating the therapeutic need to improve cardiac stress and function.20
Effects on the Renal System
Diminished blood volume and cardiac output result in decreased renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate. Other stress-induced hormones and mediators, such as angiotensin, aldosterone, and vasopressin, reduce renal blood flow further immediately after the injury. These effects result in oliguria, which, if left untreated, will cause acute tubular necrosis and renal failure. Twenty years ago, acute renal failure in burn injuries was almost always fatal. Today, however, newer techniques in dialysis have become widely used to support the kidneys during recovery. The latest reports indicate an 88% mortality rate for severely burned adults and a 56% mortality rate for severely burned children in whom renal failure develops in the postburn period. Early resuscitation decreases the risks of renal failure and improves the associated morbidity and mortality rates.10
Management
Basic Treatment
Initial Wound Care
Although prehospital management is simple, it is often difficult to enact, particularly in at-risk populations. A recent study in New Zealand21 has shown that initial first aid treatment of burns is inadequate in 60% of patients interviewed. This report also showed that inadequate first aid care is clearly associated with poorer outcomes. It was suggested that specific educational programs targeting at-risk populations might improve these outcomes.
Resuscitation
This rate should be continued until a formal calculation of resuscitation needs is performed.
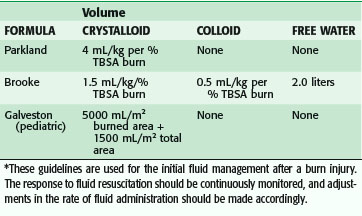
Many formulas have been devised to determine the proper amount of fluid to give a burn patient, all originating from experimental studies on the pathophysiology of burn shock. These experimental studies established the basis for modern fluid resuscitation protocols. It was shown that edema fluid in burn wounds is isotonic and contains the same amount of protein as plasma, and that the greatest loss of fluid is into the interstitium.22 Various volumes of intravascular fluid were used to determine the optimal amount in terms of cardiac output and extracellular volume in a canine burn model; this was applied to the clinical setting by the Parkland formula (Table 21-2). Plasma volume changes were not related to the type of resuscitation fluid in the first 24 hours, but thereafter colloid solutions could increase plasma volume by the amount infused. From these findings, it was concluded that colloid solutions should not be used in the first 24 hours until capillary permeability returns closer to normal. Others have argued that normal capillary permeability is restored somewhat earlier after burn (6 to 8 hours), and therefore colloids could be used earlier.
Concurrently, researchers have shown the hemodynamic effects of fluid resuscitation in burns, which culminated in the Brooke formula (see Table 21-2). It was found that fluid resuscitation causes an obligatory 20% decrease in extracellular fluid and plasma volume that concludes after 24 hours. In the second 24 hours, plasma volume returns to normal with the administration of colloid. Cardiac output is low in the first day despite resuscitation, but it subsequently increases to supernormal levels as the flow phase of hypermetabolism is established. Since these studies, it has been found that much of the fluid needs are caused by leaky capillaries that permit passage of large molecules into the interstitial space to increase the extravascular colloid osmotic pressure. Intravascular volume follows the gradient to tissues, both into the burn wound and nonburned tissues. Approximately 50% of fluid resuscitation needs are sequestered in nonburned tissues in 50% TBSA burns.
Most burn units use something similar to the Parkland or Brooke formula, which calls for administering varying amounts of crystalloid and colloid for the first 24 hours. The fluids are generally changed in the second 24 hours, with an increase in colloid use. These are guidelines to direct resuscitation of the amount of fluid necessary to maintain adequate perfusion. Studies have shown that the Parkland formula often underestimates the volume of crystalloid received in the first 24 hours after severe burn, a phenomenon termed fluid creep. No single cause has clearly been identified. More liberal use of opioid analgesic and positive pressure ventilation has been suggested.23 The increased fluid volumes are not without consequence; increased compartment pressures in the extremities, abdomen and, most recently, the orbit24 have been suggested as requiring monitoring and possible release to prevent increased morbidity and mortality. The abdominal compartment is clinically monitored via the Foley catheter. When the pressure increases toward and above 30 mm Hg, complete abdominal escharotomy is ensured and paralytics are considered. If the increased abdominal pressure persists (>30 mm Hg), an improved outcome is based on the performance of a decompressive laparotomy. However, patients who require this procedure have mortality rates of 60% to almost 100%, depending on the series. Therefore, monitoring of the resuscitation is crucial to ensure an acceptable outcome. This is easily done in burn patients with normal renal function by following the volume of urine output, which should be 0.5 mL/hr in adults and 1.0 mL/kg/hr in children. Changes in IV fluid infusion rates should be made on an hourly basis, determined by the response of the patient to the particular fluid volume administered. The exact formulas are shown in Table 21-2.
For burned children, formulas are commonly used that are modified to account for changes in surface area–to–mass ratios. These changes are necessary because a child with a comparable burn to that of an adult requires more resuscitation fluid per kilogram. The Galveston formula uses 5000 mL/TBSA burned (in m2) + 2000 mL/m2 total for maintenance in the first 24 hours. This formula accounts for maintenance needs and the increased fluid requirements of a child with a burn. All the formulas listed in Table 21-2 calculate the amount of volume given in the first 24 hours, with half is given in the first 8 hours.
Escharotomies
When deep second- and third-degree burn wounds encompass the circumference of an extremity, peripheral circulation to the limb can be compromised. The development of generalized edema beneath a nonyielding eschar impedes venous outflow and eventually affects arterial inflow to the distal beds. This can be recognized by numbness and tingling in the limb and increased pain in the digits. Arterial flow can be assessed by the determination of Doppler signals in the digital arteries and the palmar and plantar arches in affected extremities. Capillary refill can also be assessed. Extremities at risk are identified on clinical examination or on measurement of tissue pressures higher than 40 mm Hg. These extremities require escharotomies, which are releases of the burn eschar performed at the bedside by incising the lateral and medial aspects of the extremity with a scalpel or electrocautery unit. The entire constricting eschar must be incised longitudinally to relieve the impediment to blood flow completely (Fig. 21-9). The incisions are carried down onto the thenar and hypothenar eminences and along the dorsolateral sides of the digits to open the hand completely, if it is involved. If it is clear that the wound will require excision and grafting because of its depth, escharotomies are safest to restore perfusion to the underlying nonburned tissues until formal excision. If vascular compromise has been prolonged, reperfusion after an escharotomy may cause reactive hyperemia and further edema formation in the muscle, making continued surveillance of the distal extremities necessary. Increased muscle compartment pressures may necessitate fasciotomies. The most common complications associated with these procedures are blood loss and the release of anaerobic metabolites, causing transient hypotension. If distal perfusion does not improve with these measures, central hypotension because hypovolemia should be suspected and treated.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree