Bilateral Mediastinal Mass
Toms Franquet, MD, PhD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Mediastinal Lipomatosis
Normal and Hyperplastic Thymus
Thyroid Goiter
Lymphoma
Germ Cell Tumors
Less Common
Lymphangioma
Extramedullary Hematopoiesis
Rare but Important
Liposarcoma
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Most common cause of diffuse mediastinal widening is mediastinal lipomatosis
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Mediastinal Lipomatosis
Large amounts of normal fat; smooth symmetrical mediastinal widening without mass effect
Associated with Cushing syndrome, steroid treatment, and obesity
Normal and Hyperplastic Thymus
Normal: Generalized thymic enlargement (< 5 years old)
Hyperplasia: Immunologic rebound phenomenon
Thyroid Goiter
Most common cause of tracheal deviation; anterosuperior or posterosuperior mediastinal mass
Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Bulky, bilaterally asymmetrical, mediastinal-hilar adenopathy
Hodgkin lymphoma: Due to nodal aggregation; rounded or bulky soft tissue masses; prevascular and paratracheal nodes
Germ Cell Tumors
Teratoma: Multiple tissue densities
Nonseminomatous GCT: Large, irregular-shaped anterior mediastinal mass; pleural effusions and pulmonary metastasis common
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Lymphangioma
Unilocular or multilocular (30%); may insinuate around normal structures
Low signal intensity on T1WI; high signal intensity on T2WI
Extramedullary Hematopoiesis
Compensatory phenomenon due to inadequate production or excessive destruction of blood cells, e.g., sickle cell disease
Paravertebral masses: Single or multiple; unilateral or bilateral
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Liposarcoma
Rare malignant mediastinal tumor
Image Gallery
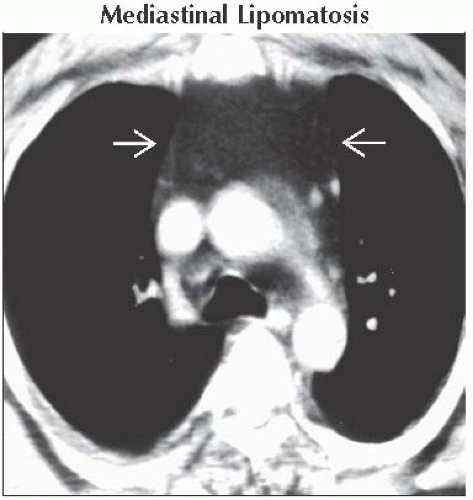 Axial CECT shows abundant homogeneous mediastinal fat that displaces the anterior junction line laterally
 without mass effect on adjacent vascular structures. without mass effect on adjacent vascular structures.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|