Aortic Intramural Abnormality
Gregory Kicska, MD, PhD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Atherosclerosis/Adherent Thrombus
Aortic Dissection
Less Common
Aortic Intramural Hematoma
Penetrating Atherosclerotic Ulcer
Rare but Important
Takayasu/Giant Cell Arteritis
Radiation
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Aortic wall should measure < 4 mm
Aortic wall should be isointense to lumen
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Atherosclerosis/Adherent Thrombus
Concentric diffuse involvement vs. spiral involvement of intramural hematoma
Aorta often tortuous with atherosclerotic disease in branch vessels
Aortic Dissection
Intimal flap readily seen on contrast CT as unenhanced line through lumen
Intraluminal calcifications on noncontrast CT suggest diagnosis and represent displaced intimal calcifications
“Beak” sign: False lumen side of dissection flap meets outer wall with acute angle
“Cobweb” sign: False lumen traversed by media fibers
Confusion with pulsation artifact at aortic root avoided by inspecting coronal images
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Aortic Intramural Hematoma
Hyperdense aortic wall compared to lumen when acute, isodense when old
Check LV chamber for hypodense blood to avoid pitfall of confusion anemia
Patient more likely to progress to dissection with coexistence of ulcer-like projections
Most commonly in descending aorta
Penetrating Atherosclerotic Ulcer
Luminal irregularity
Must extend beyond expected contour of intima
Outer aortic wall thickening indicates acuity
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Takayasu/Giant Cell Arteritis
Radiographically indistinguishable, differentiated based on age (Takayasu < 50 years, giant cell > 50 years)
FDG PET can determine active disease
Aortic caliber will be reduced
Subclavian stenosis is hallmark finding
Pulmonary artery strictures and mesenteric vessel stenosis are common
Radiation
Vascular calcifications confined to radiation field
Radiation history will be present
Image Gallery
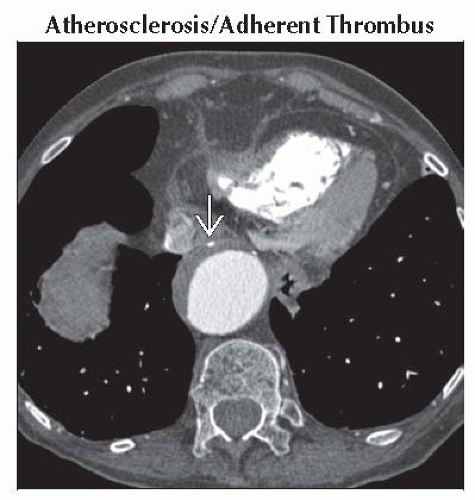 Axial enhanced CT shows mural thrombus in an otherwise dilated aorta. Note that intimal calcifications are on the outer edge of the thrombus
 . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|