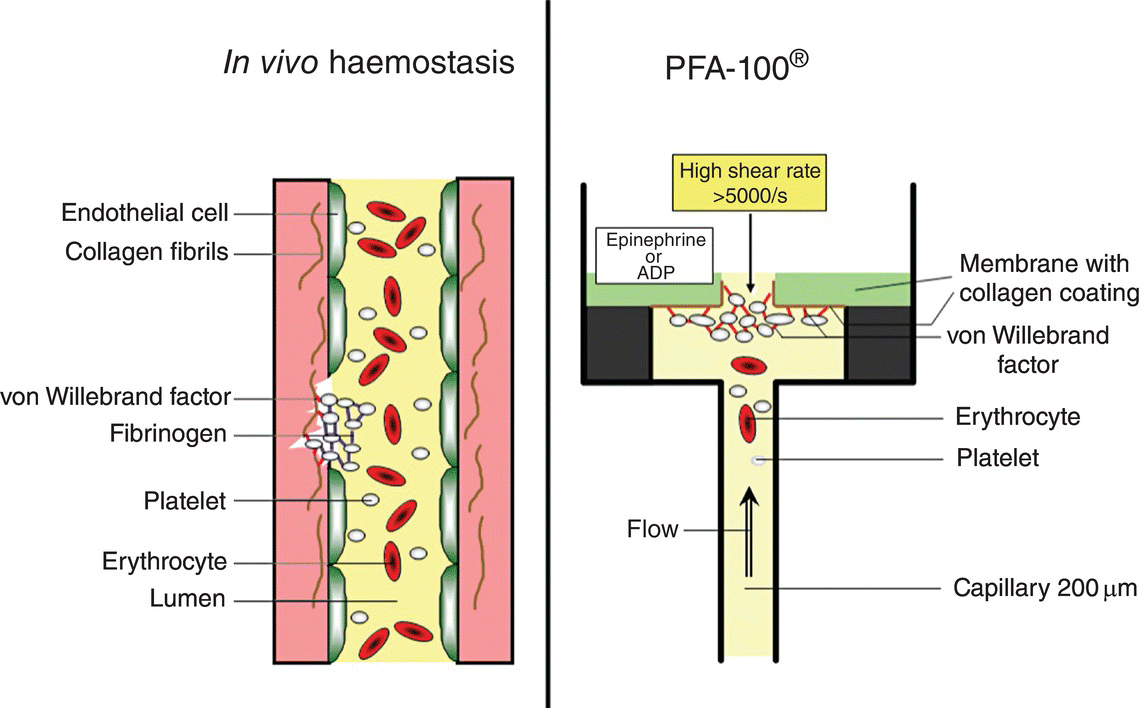
11 Nicoline J. Breet and Jurriën M. ten Berg St Antonius Hospital, Nieuwegein, The Netherlands The PFA-100® system (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Products GmbH, Germany) measures platelet function, in particular adhesion and aggregation, in whole blood under high shear conditions (5000/s) [1]. A constant vacuum of 40 mBar is maintained in the system that mimics the pressure in a capillary in the human body [2]. The time needed to form a platelet plug occluding the aperture cut into a membrane coated with an agonist is determined and reported as closure time (CT) in seconds, which is inversely related to platelet reactivity. If the formed clot is too weak, the CT cannot be measured and the results are presented as greater than 300 s [2] (Figure 11.1). Figure 11.1 Schematic presentation of the PFA-100 system. The time needed to form a platelet plug occluding the aperture cut into a collagen/epinephrine (COL/EPI) or collagen/ADP (COL/ADP)-coated membrane is determined and reported as closure time (CT) in seconds. Various types of cartridges are available. The membrane of the classic cartridge is coated with either collagen and epinephrine (COL/EPI) or collagen and adenosine diphosphate (COL/ADP) as agonists. The COL/EPI test cartridge detects intrinsic platelet defects, von Willebrand disease, as well as exposure to platelet-inhibiting agents such as aspirin. The COL/ADP test cartridge is less influenced by aspirin use. Recently, a novel PFA-100® test cartridge has been introduced, the final prototype of INNOVANCE® PFA P2Y*. This novel test cartridge intents to measure the effect of P2Y12 receptor blockers on platelet function [3]. The PFA-100 is a simple and semiautomated assay that uses whole blood. It mimics the in vivo process of thrombus formation by inducing shear stress. However, several studies have demonstrated that the COL/ADP cartridge is relatively insensitive to the effect of P2Y12 receptor blocker treatment [4]. This might be attributed to the relatively high local concentration of collagen (6 µg/mL) and ADP (0.5 mmol/L) in the cartridge, under which circumstances clopidogrel might be unable to inhibit the formation of the platelet plug [5, 6]. Furthermore, since the assay is highly affected by the levels of von Willebrand factor (vWF) and hematocrit [5, 6], high vWF levels might mask the inhibitory effects of clopidogrel because the shear stress will lead to instant binding of vWF to glycoprotein (GP)IIb/IIIa [5]. The relation between the PFA COL/EPI cartridge and the arachidonic acid (AA)-induced light transmittance aggregometry is good [7]. Multiple studies have described the ability of the PFA COL/EPI cartridge in monitoring the efficacy of aspirin-induced antiplatelet effect [8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]. Nevertheless, contrasting results have been reported concerning the predictive accuracy of this cartridge. Some studies demonstrated a two- to fivefold [16, 17, 18] higher risk in aspirin-treated patients with a shorter CT, using either a cutoff value of 193 or 300 s, whereas the largest study thus far demonstrated no association at all between high on-aspirin platelet reactivity (HAPR) according to the PFA COL/EPI and adverse clinical outcome [19]. A meta-analysis on the predictive value of a short CT as established by the PFA COL/EPI cartridge in aspirin-treated patients demonstrated an odds ratio of 2.1 (95% CI, 1.4–3.4) of HAPR in the eight prospective studies of varying patient populations with different clinical scenarios, using cutoff values varying between 170 and 203 (n = 1227). In contrast, in the meta-analysis on nonprospective studies, no association between HAPR according to the PFA COL/EPI and clinical outcome was established (n = 1466) [16]. Some issues merit careful consideration. Since there are no recommended cutoffs, the cutoff values in the studies included in this meta-analysis were not based on clinical outcome and thus can be questioned. In addition, the study with the highest odds ratio used the relatively subjective clinical end point angina (either as single end point or as part of a combined end point) [15]. Furthermore, the studies establishing a higher odds ratio in patients with HAPR all included higher-risk patients (presenting with an acute coronary syndrome (ACS)). In addition, the largest studies thus far that demonstrated no association between HAPR according to the PFA COL/EPI and adverse clinical outcome were not included in the current meta-analysis [19, 20]. In the first study, a prospective study of 700 aspirin-treated patients presenting for angiographic evaluation of coronary artery disease, it was demonstrated that HAPR as assessed by the PFA COL/EPI cartridge using the manufacturer’s advised cutoff of 193 s did not correlate with the subsequent major adverse cardiovascular events (defined as all-cause death, cardiovascular death, and a combined end point including cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction (MI), hospitalization for revascularization, or ACS). This is in line with the observations of the POPular study (n = 719), in which the PFA COL/EPI was also unable to discriminate between patients with and without primary end point (a composite of all-cause death, nonfatal myocardial, stent thrombosis (ST), and ischemic stroke), both using the currently accepted cutoff value of 193 s as the cutoff established by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and set at 277 s. Both studies were performed in a relatively low-risk population, undergoing elective PCI with stent implantation, and excluded higher-risk patients (in particular ST-elevation MI). As the PFA-100 mimics the in vivo process of thrombus formation by inducing shear stress, it might be considered a better model for ACS rather than stable ischemia. Clinical evaluation of the PFA-100 COL/ADP in monitoring P2Y12 receptor blocker therapy is limited. Several studies have demonstrated a slight but nonsignificant prolongation of the CT with the COL/ADP cartridge after clopidogrel administration, suggesting that this cartridge might not be suitable for monitoring therapy with P2Y12 receptor blockers [4, 21, 22, 23]. This is in line with the observation of the POPular study, the only study thus far describing performance data of the cartridge in a large cohort of patients undergoing elective PCI [24]. The PFA-100 COL/ADP cartridge (n = 812) was unable to discriminate between patients with and without ischemic events at 1-year follow-up. The POPular study was the first to report performance data of the prototype INNOVANCE® PFA P2Y, which in its final design became available halfway through the inclusion period. Although the sample size has insufficient statistical power (n = 588), the survival analysis demonstrated a lower incidence of the primary end point in patients without high on-treatment platelet reactivity. However, the addition of high on-treatment platelet reactivity as measured with INNOVANCE® PFA P2Y to a statistical model containing traditional Framingham and procedural risk factors did not improve the predictability of the risk model (as measured by an increase in the area under the curve). Thus, the novel cartridge seems promising for the evaluation of the efficacy of P2Y12 inhibition [24], but its utility as a predictor of cardiovascular events still requires further investigation. To date, little data are available on the PFA-100® system in patients on GPIIb/IIIa receptor inhibitors (GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors) [25, 26]. Madan et al. demonstrated that the PFA-100 provides similar qualitative information on platelet inhibition as light transmission aggregometry [27]. Still, as almost all patients achieved a maximal CT, the useful range of the assay is limited [28]. In addition, there are no studies available addressing the relation between CT as established by the PFA COL/EPI or PFA COL/ADP and clinical outcome in patients on GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors. Although this test can be used in the catheterization laboratory and the reproducibility between laboratories is good, data on its predictive value in patients on aspirin is conflicting. In addition, its use in predicting clinical outcome patients on P2Y12 receptor blockers seems promising but remains to be confirmed by other studies. Therefore, we consider the PFA not suitable for use in daily clinical practice yet.
Shear Stress-Based Platelet Function Tests
PFA-100
Description of the test: General concepts
Strengths and weaknesses of the test
Validity of the test in measuring antiplatelet effect and predicting clinical outcomes
Aspirin
Clopidogrel
Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitors
Conclusion
IMPACT-R
Description of the test: General concepts
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


