Wide and Narrow Complex Tachyarrhythmias
David V. Daniels
Amin Al-Ahmad
BACKGROUND AND APPROACH
The tachyarrhythmias presented in this chapter and the approach to their differential diagnosis, workup, and treatment are among the most common problems encountered in inpatient cardiology. These entities range in gravity from arrhythmias that are a nuisance, allowing for careful consideration as to the best approach, to life-threatening emergencies demanding decisive action.
DEFINITIONS
Narrow complex tachycardia: QRS duration <120 milliseconds
Wide complex tachycardia: QRS duration >120 milliseconds with or without pre-excitation
Pre-excitation: Initial “slurring” of the QRS complex implying manifest antegrade conduction down an accessory bypass tract (e.g., WPW pattern); may see in sinus rhythm atrial fibrillation (AF), or antidromic reciprocating tachycardia (ART)
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT): A tachycardia arising from or involving the atria, specialized atrial conduction tissue, or compact A-V node
Though technically SVT includes AF, some exclude AF as a separate entity for the purposes of nomenclature for multiple reasons
Ventricular tachycardia (VT): A tachycardia arising from and exclusively involving the tissue beneath the compact portion of the AV node, including the His bundle, bundle branches, and ventricular myocardium
VT most commonly associated with CAD and/or structural heart disease
HISTORY
Symptoms include palpitations, dyspnea, chest pain, presyncope, syncope
History of myocardial infraction (MI), congestive heart failure (CHF) increase the risk of malignant arrhythmias such as VT
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) → consider VT
Drop attack (sudden syncope without prodrome) is suggestive of cardiac mediated syncope but its absence should not dissuade you from considering the diagnosis4
Palpitations are also commonly felt in the recovery phase of neurocardiogenic syncope
Consider the patient’s medications as an etiology of arrhythmias:
A-V nodal agents—see bradyarrhythmias
Antiarrhythmics—particularly those that prolong the QTc, IC agents (Flecainide, encainide (not available in the United States), propafenone), dofetilide, sotalol, amiodarone
QTc-prolonging nonantiarrhythmics—macrolides, fluoroquinolones, antipsychotics, etc.
Digoxin toxicity
PHYSICAL EXAM
Hypotension or clinical instability does not distinguish between SVT and VT!
Cannon A waves may be observed in the jugular venous pulse and in the setting of a wide complex tachycardia are indicative of A-V dissociation and highly suggestive of ventricular tachycardia
Crackles or wheezes may suggest heart failure but also consider concomitant pulmonary disease that may be associated with atrial tachycardias
Examine chest wall for the presence of an ICD or pacemaker that you can interrogate to reveal the atrial rhythm in difficult cases
Murmurs may point to cardiac disease in general, which is useful, but an S3 is suggestive of decompensated heart failure and can be the cause or result of an arrhythmia
INITIAL MANAGEMENT
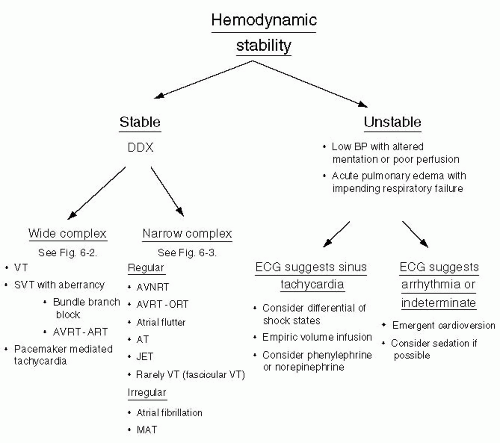
Always consider cardioversion for unstable arrhythmias. (See Figure 6-1.)
Obtain a baseline ECG for comparison whenever possible!
Attention to electrolyte abnormalities, especially ↓ K+ and Mg2+
If the patient has an ICD or pacemaker (particularly dual chamber), consider interrogation to help with workup of the arrhythmia
WIDE COMPLEX TACHYCARDIA (WCT)
Differential diagnosis includes VT versus SVT with aberrancy or pre-excited tachycardias. (See Table 6-1.)
Unselected population 80% of WCT = VT
Post-MI or structural heart disease 95% of WCT = VT5
Consider AF with antegrade conduction down an accessory pathway (pre-excited AF) if irregular with wide complex—avoid A-V nodal blockers can → VF
Misdiagnosis of a WCT as SVT when it is VT can have several consequences:
Acute progressive pump failure possible with incessant VT
Drugs: Verapamil, diltiazem, adenosine are potentially dangerous in VT
Failure to consider acute ischemia as an etiology of new onset VT
TABLE 6-1 Wide complex tachycardia: Differentiating VT from SVT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree