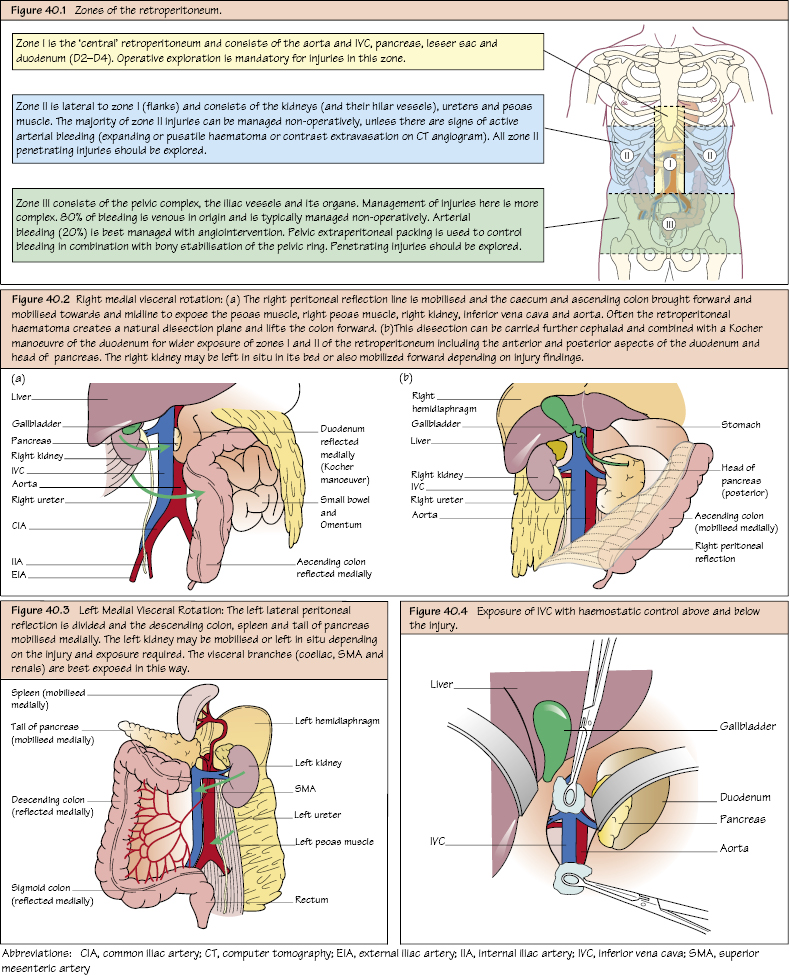
Vascular Trauma: Abdomen and Pelvis These are associated with a very high mortality and morbidity (including pancreatic, biliary and duodenal injuries), mostly due to massive haemorrhage. Management is dependent on which of the three distinct anatomical zones is involved (see Figure 40.1). Zone 1 haematoma (adjacent to the great vessels) on CT scanning or intra-operatively mandates further operative exploration! This carries a very high mortality (>80%) with most dying before reaching hospital! Proximal control of the aorta can be performed via a transperitoneal (infrarenal) or supracoeliac approach (through the lesser sac). Although quickest for control, supracoeliac clamping >60 minutes in trauma has a near 100% mortality! If in extremis, proximal control should be via a left lateral thoracotomy. During surgery, the best exposure is with a left medial visceral rotation.
Retroperitoneal (RP) Injuries
Investigation Versus Immediate Management
Investigations
Zone 1 RP Injury
Abdominal Aorta
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


