Unusual Types of Accessory Pathways
Introduction
Typical accessory pathways (APs) (bundle of Kent) are nondecremental muscle fibers spanning the tricuspid or mitral annulus. In contrast to single APs, multiple APs produce unusual patterns of ventricular preexcitation and/or retrograde atrial activation with both orthodromic and antidromic tachycardia circuits. Atypical APs include those exhibiting decremental conduction and/or originate/insert into the atrio-ventricular (AV) node-His-Purkinje axis (e.g., nodo-fascicular [NF] AP).
The purpose of this chapter is to:
Discuss the 12-lead ECG and electrophysiologic clues to the presence of multiple APs.
Describe the electrophysiologic features of the permanent form of junctional reciprocating tachycardia (PJRT).
Describe the electrophysiologic features of APs that originate/insert into the AV node-His-Purkinje axis.
MULTIPLE APs
Multiple APs can cause different orthodromic reciprocating tachycardia (ORT) and antidromic reciprocating tachycardia (ART) circuits. Antidromic reciprocating tachycardia itself should raise suspicion that more than one AP is present.1,2 Right free wall and posteroseptal APs are a frequent combination, and Ebstein’s anomaly is associated with multiple APs perhaps due to abnormal development of the tricuspid annulus.2 Several 12-lead ECG and electrophysiologic clues indicate the presence of multiple APs.
12-LEAD ECG
Electrocardiographic clues to the presence of multiple APs include 1) an atypical or unusual pattern of preexcitation not explained by a single AP, 2) ≥2 preexcited QRS morphologies, 3) ≥2 P-wave morphologies during ORT, and 4) spontaneous change from ORT to preexcited tachycardia (ORT with bystander preexcitation).3,4,5 Two or more preexcited QRS morphologies might be observed during atrial fibrillation and simulate polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, occur during different preexcited tachycardias, or follow administration of procainamide or ajmaline due to selective block in one AP.
ELECTROPHYSIOLOGIC STUDY
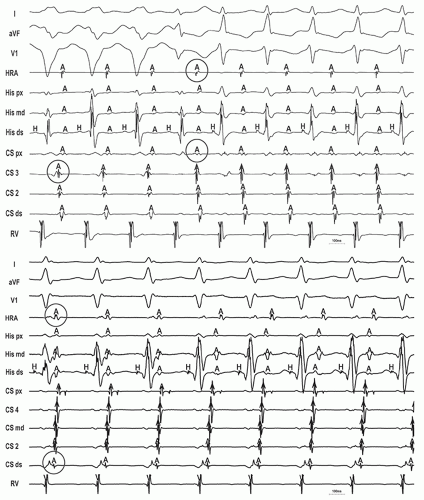
Electrophysiologic clues to the presence of multiple APs include 1) antegrade-retrograde mismatch (discrepancy between the earliest site of ventricular activation during manifest preexcitation and atrial activation during ORT), 2) ≥2 preexcited QRS morphologies, 3) ≥2 atrial exit sites or atrial activation patterns during ORT, and 4) antidromic tachycardia with retrograde conduction over another AP (duodromic tachycardia) (Figs. 11-1, 11-2 and 11-3).3,4,6,7
PERMANENT FORM OF JUNCTIONAL RECIPROCATING TACHYCARDIA
PJRT is a nearly incessant form of long RP ORT using a concealed, slowly conducting, decremental AV AP (see Chapter 6).8,9,10,11,12,13 Its incessant behavior can cause a tachycardia-mediated cardiomyopathy. These APs are classically located in the posteroseptal region near the ostium (os) of the coronary sinus (CS), but other locations have been reported.10 Absence of manifest preexcitation during sinus rhythm has been attributed to repetitive retrograde concealment from the AV node-His-Purkinje system into the AP with prolonged antegrade refractoriness rather than “impedance mismatch” at the AP ventricular insertion site because manifest preexcitation can develop with AV block.11 A sinuous, tortuous course within the posterior pyramidal space causing changes in axial resistivity might explain its rate-dependent properties.11
ELECTROPHYSIOLOGIC FEATURES
12-lead ECG
The characteristic 12-lead ECG of PJRT is a regular, long RP narrow complex tachycardia with inverted P waves inferiorly
and slightly positive P waves in V1 (due to AP location near the CS os) (see Fig. 6-3).9
and slightly positive P waves in V1 (due to AP location near the CS os) (see Fig. 6-3).9
Electrophysiologic Study
The ventriculo-atrial (VA) interval is long, and the earliest site of retrograde atrial activation is typically near the os of the CS (see Figs. 6-8, 6-9 and 6-10).9,11 A 1:1 AV relationship is mandatory.
ZONES OF TRANSITION
Initiation
Unlike classic ORT, induction of PJRT can occur spontaneously during sinus rhythm without the need for prematurity, which contributes to its incessant behavior (Fig. 11-4).9 Initiation is dependent on achieving a critical sinus rate and not necessarily
on a critical AV delay. Because the slow and decremental retrograde properties of the AP allow it to continually accept sinus impulses conducting over the AV node-His-Purkinje system, tachycardia is triggered when block occurs antegradely in the AP (e.g. AP-V interface) at a critical sinus rate.
on a critical AV delay. Because the slow and decremental retrograde properties of the AP allow it to continually accept sinus impulses conducting over the AV node-His-Purkinje system, tachycardia is triggered when block occurs antegradely in the AP (e.g. AP-V interface) at a critical sinus rate.
Termination
The obligatory 1:1 AV relationship implies that PJRT terminates with either AV or VA block. Spontaneous termination with AV block excludes atrial tachycardia (AT). Termination by earlycoupled ventricular premature depolarizations (VPDs) with VA block also excludes AT. Termination by His refractory VPDs with VA block excludes both pure atypical AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) and AT (but not NF reentrant tachycardia [NFRT] or atypical AVNRT with a bystander NF AP inserting into the slow pathway [SP]) (Fig. 11-5; see also Figs. 6-11 and 6-12).
PACING MANEUVERS FROM THE VENTRICLE
His Refractory VPD
Entrainment from the Ventricle
Ventricular overdrive pacing accelerates PJRT to the pacing cycle length and the response to entrainment is “AV.”16 Slow retrograde AP conduction, however, can produce pseudo “AAV” responses yielding a false diagnosis of AT (Fig. 11-7; see also Fig. 6-14). Entrainment with orthodromic capture of the His bundle indicates the presence of an AP (see Fig. 2-6). While PJRT can cause post-pacing interval (PPI) − tachycardia cycle length (TCL) ≤115 ms, corrected PPI <110 ms, ΔHA (HA[entrainment] − HA[SVT]) <0, and ΔVA (SA − VA) ≤85 ms, significant decrement in the AP can also generate large values for all these criteria yielding a false diagnosis of atypical AVNRT (Figs. 11-7, 11-8 and 11-9).17,18,19,20,21
Onset of Ventricular Overdrive Pacing
Similar to classic ORT, PJRT can be reset (advanced or delayed) or terminated by paced ventricular complexes within the transition zone (the equivalent of a His refractory VPD) (Fig. 11-10).
ACCESSORY PATHWAYS ORIGINATING/INSERTING INTO THE AV NODE-HIS-PURKINJE SYSTEM
Atrio-nodal (James fibers) and atrio-His AP are rare. ORT, using a concealed atrio-nodal AP, shares features common to 1) AT (eccentric atrial activation [particularly, right-sided] and peristence despite AV block [block distal to the nodal input]), 2) AVNRT (long PPI following entrainment from the ventricle, no effect by His refractory VPDs), and 3) ORT (eccentric VA conduction during ventricular pacing).22,23 Clues to an atrio-His AP include 1) short AH (PR) interval, 2) lack of AH prolongation (decremental conduction) with premature atrial stimulation, and 3) rapid ventricular rates during supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)/atrial tachyarrhythmias.24 Mahaim fibers refer collectively to variant APs that share several common electrophysiologic features: 1) classic origin (e.g., AV node) and/or insertion in (nodo-fascicular [NF]) or near (nodo-ventricular [NV]) the right bundle (RB) causing typical LBBB QRS complexes (although left-sided fibers have also been reported), 2) rate-dependent (decremental), antegrade-only conduction (although concealed retrogradely, conducting NF/NF APs have been described), and 3) minimal (fasciculo-ventricular) or even absent (NF/NV or atrio-fascicular [AF]) preexcitation during sinus rhythm (because of slow antegrade AP conduction) exposed only by atrial pacing or during antidromic tachycardia (latent AP). These include nodo-fascicular/nodo-ventricular, atrio-fascicular (or a long AV fiber inserting near the RB), and fasciculo-ventricular APs. Nodofascicular/nodo-ventricular APs originate in the AV node (often SP) and insert into the antero-apical region of the right ventricle in or near the RB. Atrio-fascicular (or long AV) APs originate along the lateral tricuspid annulus (posterolateral to anterolateral region) and insert in or near the RB. Fasciculo-ventricular APs originate in the RB and insert into the right ventricle.
NODO-FASCICULAR/NODO-VENTRICULAR AP
Electrophysiologic Features
The HV interval can be normal, and baseline preexcitation is often absent.25,26 Decremental atrial pacing or atrial extrastimulation reveals typical LBBB preexcitation with prolonging St-delta intervals because of decremental conduction over the AP. During maximal preexcitation, block in the AV node distal to origin of the AP causes exclusive conduction over the AP with subsequent retrograde activation of the His bundle (“VH” interval). Further shortening of the atrial pacing cycle length or coupling interval causes increase in the St-delta interval, but the VH interval and degree of preexcitation remain the same. Because the AP bypasses the His bundle, His bundle extrasystoles normalize the QRS complex if preexcitation is present (unless the extrasystoles arise from the AV node proximal to the nodal origin of the AP).26 Parahisian pacing can differentiate a nodo-fascicular (“AV nodal response”) from a nodo-ventricular AP (“AP response”).27,28
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree