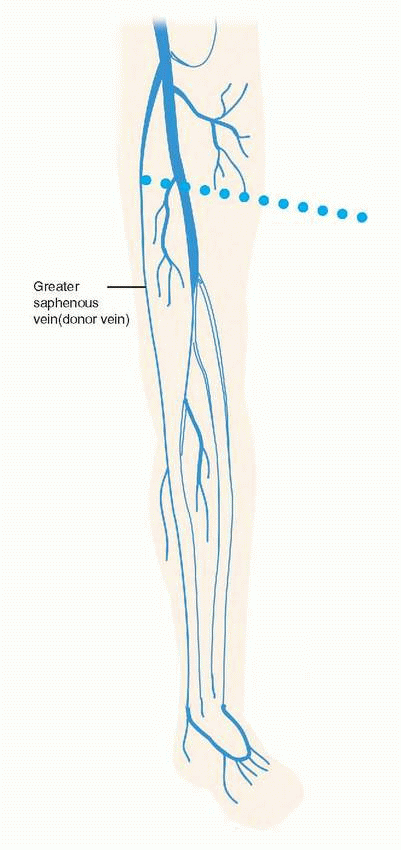
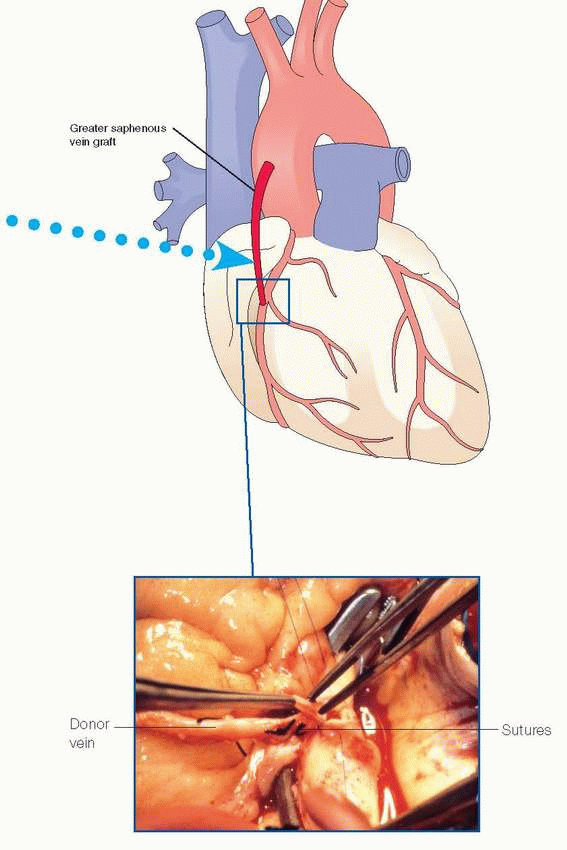
|
|
Class | Features | Rhythms treated | Examples |
I Sodium channel blockers | ♥ Largest class ♥ Three subdivisions plus adenosine ♥ Decrease automaticity, conduction velocity, and membrane responsiveness | ♥ IA: atrial and ventricular arrhythmias ♥ IB: acute ventricular arrhythmias ♥ IC: severe refractory ventricular arrhythmias ♥ Adenosine: paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia | ♥ IA: disopyramide (Norpace) ♥ IB: lidocaine (Xylocaine) ♥ IC: flecainide (Tambocor) |
II Betaadrenergic blockers | ♥ Slow automaticity of sinoatrial (SA) node ♥ Reduce conduction of atrioventricular (AV) node and pacer cells ♥ Decrease strength of contraction | ♥ Atrial flutter and fibrillation ♥ Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia | ♥ Atenolol (Tenormin) ♥ Metoprolol (Lopressor) ♥ Propranolol (Inderal) ♥ Carvedilol (Coreg) ♥ Nebivolol (Bystolic) |
III Diverse group | ♥ Mechanism of action poorly understood ♥ May slow repolarization ♥ May prolong refractory period | ♥ Ventricular arrhythmias | ♥ Amiodarone (Cordarone) ♥ Dofetilide (Tikosyn) ♥ Sotalol (Betapace) ♥ Ibutilide (Corvert) |
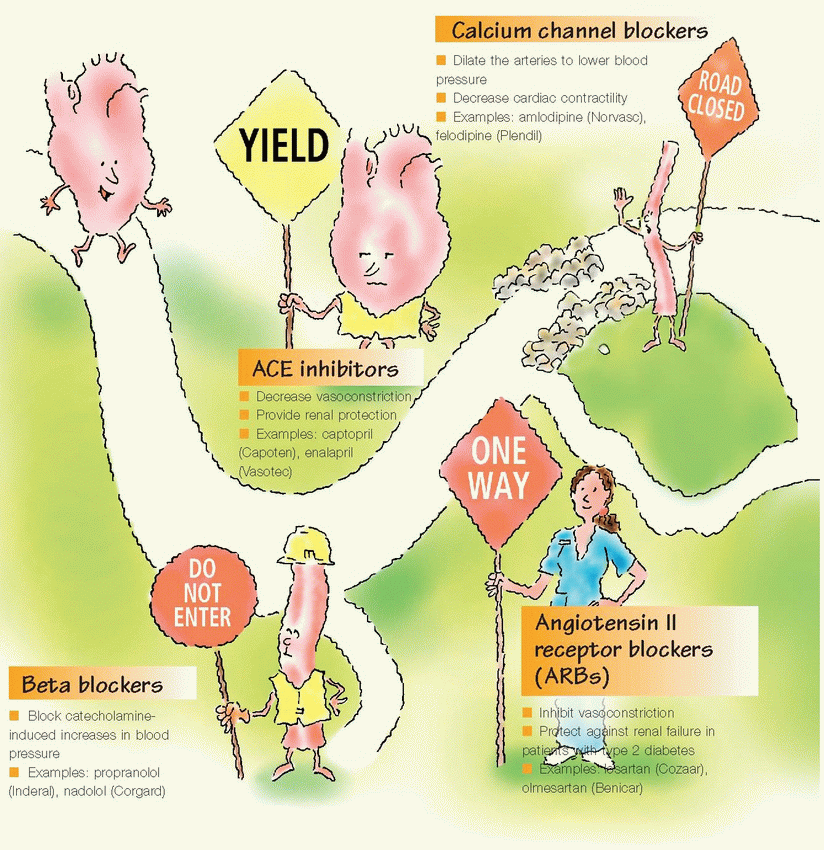
IV Calcium channel blockers | ♥ Decrease cardiac contractility and oxygen demand ♥ Dilate coronary arteries and arterioles | ♥ Supraventricular arrhythmias with rapid ventricular response | ♥ Diltiazem (Cardizem) ♥ Nifedipine (Procardia) ♥ Verapamil (Calan) |
digoxin (Lanoxin), which slows the heart rate and electrical impulse conduction through the SA and AV nodes
phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors, which provide short-term management of heart failure or long-term management in patients awaiting heart transplant surgery. Two examples of PDE inhibitors are inamrinone and milrinone.
|
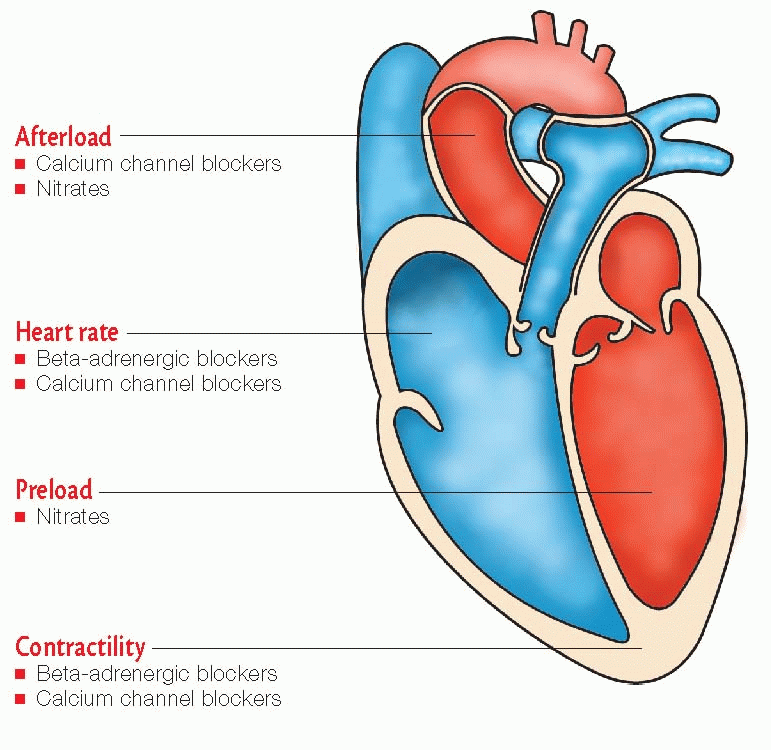
nitrates (used primarily to treat acute angina)
beta-adrenergic blockers (prescribed for long-term prevention of angina)
calcium channel blockers (used when other drugs fail to prevent angina).
|
|
|
|
|
Headache
Fatigue
Angioedema
Gl reactions
Electrolyte imbalance (specific to drug used)
Altered renal function when used with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Dry, nonproductive, persistent cough
Transient elevations of blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine levels
Cough
Tickling in throat
Dizziness
Fainting
Diarrhea
Lower total cholesterol levels
Example: ezetimibe (Zetia)
Water-soluble vitamin
Lowers triglyceride levels
Increases high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels
Example: niacin (Niacor)
|
Remove excess bile acids from fat deposits
Lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels
Example: cholestyramine (Questran)
Lower triglyceride levels
Minimally increase HDL levels
Examples: fenofibrate (Tricor), gemfibrozil (Lopid)
Also known as statins
Lower total cholesterol and LDL levels
Minimally increase HDL levels
Examples: atorvastatin (Lipitor), simvastatin (Zocor), rosuvastatin (Crestor)
Category | Features | Examples |
Heparins | ♥ Used in patients with unstable angina, Ml, and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) ♥ Act immediately when given I.V. ♥ Available in regular and low-molecular-weight forms | ♥ Heparin (Liquaemin) Low-molecular-weight ♥ Dalteparin (Fragmin) ♥ Enoxaparin (Lovenox) |
Coumarin derivative | ♥ Antagonizes production of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors ♥ Prevents DVT ♥ Used in patients who have undergone prosthetic heart valve surgery and those with diseased valves ♥ Given orally and takes days to reach effect | ♥ Warfarin (Coumadin) |
Antiplatelet drugs | ♥ Prevent thromboembolism | ♥ Aspirin ♥ Clopidogrel (Plavix) |
Direct thrombin inhibitors | ♥ Treat heparin-induced thrombocytopenia ♥ Used when heparin can’t be ♥ Prophylactically used before angioplasty and stent placement ♥ Available I.V. | ♥ Argatroban ♥ Bivalirudin (Angiomax) ♥ Lepirudin (Refludan) |
Glycoprotein llb/Ilia inhibitors | ♥ Used in patients with unstable angina and before and during angioplasty ♥ Prevent platelets from binding together ♥ Available I.V. | ♥ Abciximab (ReoPro) ♥ Eptifibatide (Integrilin) ♥ Tirofiban (Aggrastat) |
|
|
|
 photo op
photo op
|
|
|
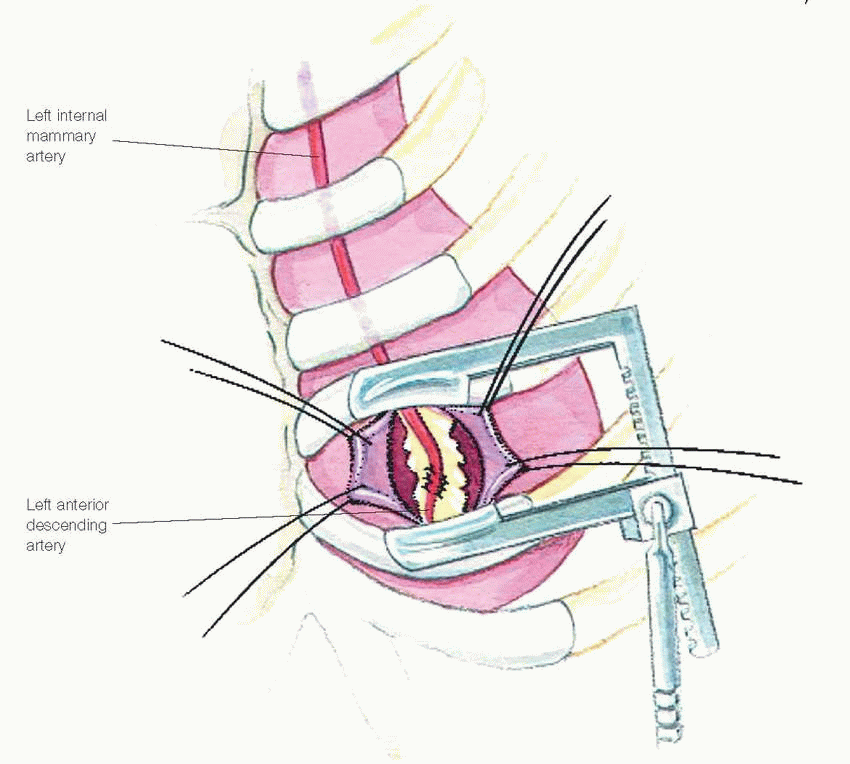
Features | On-pump CABG | OPCAB | MIDCAB |
Access site | ♥ Breastbone severed for heart access | ♥ Breastbone severed for heart access | ♥ Incisions made between ribs for anterior heart access, no bones cut |
Indications | ♥ Suitable for multivessel disease, any coronary artery | ♥ Suitable for multivessel disease, any coronary artery | ♥ Only used for one-vessel diseases in anterior portions of heart, such as left anterior descending artery, or some portions of the right coronary and circumflex arteries |
Graft types | ♥ Combination of artery and vein grafts | ♥ Combination of artery and vein grafts | ♥ Arterial grafts (better long-term results) |
Complications | ♥ Highest risk of postoperative complications | ♥ Reduced blood usage, fewer rhythm problems, less kidney dysfunction than on-pump CABG |