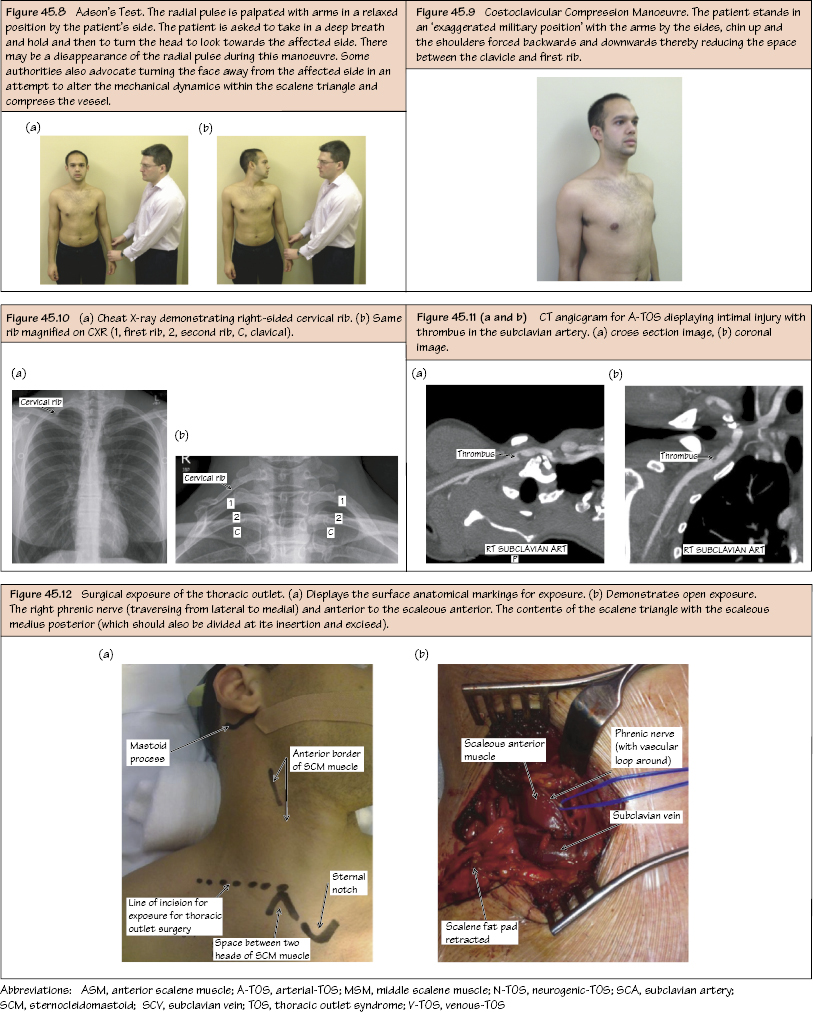
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a neurovascular compression at the level of the thoracic outlet. There are numerous causes including abnormal angulation of first rib, congenital cervical rib, scalene muscle hypertrophy, abnormality at the level of the scalene tubercle (congenital or acquired) and post-trauma (e.g. malunion of clavicle fracture). It has a female preponderance (3 : 1) The causes and sites of compression are shown in Figures 45.3–45.5. Neurogenic (N-TOS) – 95%. Venous (V-TOS) – 3%. Arterial (A-TOS) – 2%. Within the scalene triangle Beyond the scalene triangle Junction of thorax with the base of neck bounded by: Within the thoracic outlet is the scalenus anterior muscle, with the subclavian vein in front, the scalenus medius muscle (with the subclavian artery and brachial plexus between the two muscles). Boundaries
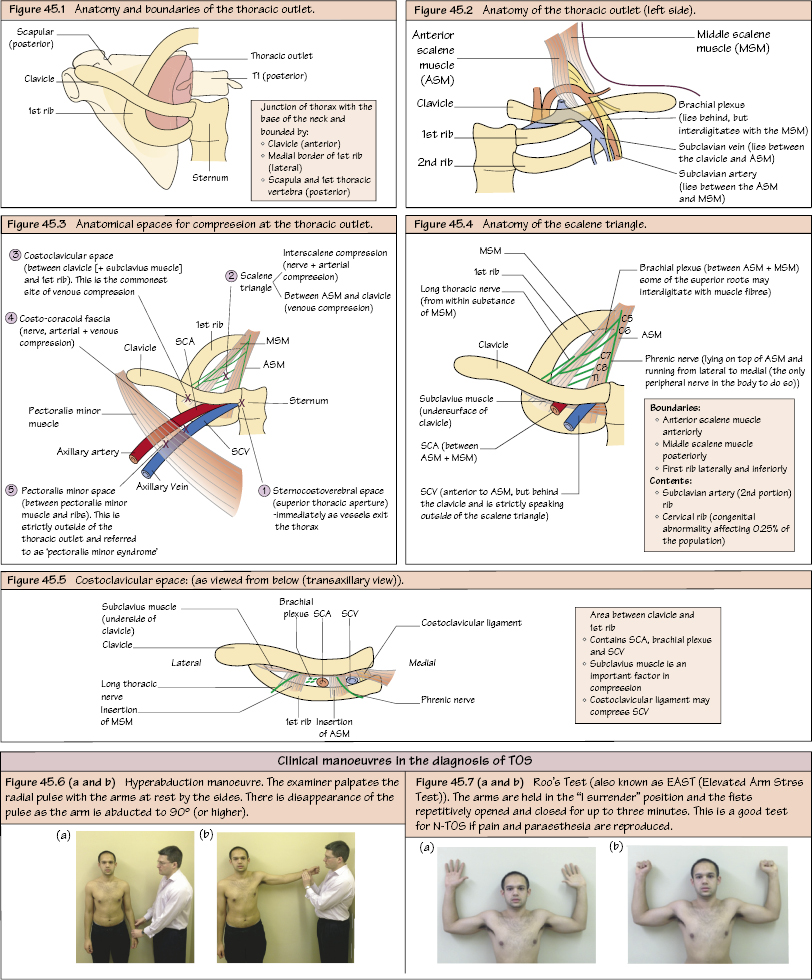
Aetiology
Classification
Anatomical Spaces for Compression
Causes of compression
Anatomy of the Thoracic Outlet
Anatomy of Scalene Triangle
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


