1. Branch and peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis
6. Surgically created shunts
(a) Blalock-Taussig
(a) Post surgical
(b) Central
(b) Native
(c) Sano
2. Pulmonary vein stenosis
7. Systemic vein stenosis
(a) Post surgical repair of TAPVD
(a) Post surgical (Fontan, Senning, Mustard)
(b) Native
(b) Pacemaker electrodes, central lines
3. Aorta and branches
(a) Native coarctation
8. Major aorto-pulmonary collateral arteries (MAPCAs)
(b) Recoarctation
9. Intracardiac communications
(i) Surgery
(a) Atrial septum
(ii) Balloon dilation
(b) Atrial fenestration
(c) Aneurysms
(d) Abdominal coarctation
10. Sealing of fistula or communication with covered stent
4. Right ventricle outflow tract
(a) Patent arterial duct
(a) Pulmonary atresia after perforation
(b) AV fistula
(c) Fontan fenestration
(b) Tetralogy of Fallot
11. Coronary artery stenosis
(c) Conduits
(i) Standalone
(a) Kawasaki
(b) Post arterial switch
(ii) Preparation for percutaneous valve implantation
(c) Left internal mammary bypass
5. Arterial duct in duct-dependent
(a) Pulmonary circulation
(b) Systemic circulation
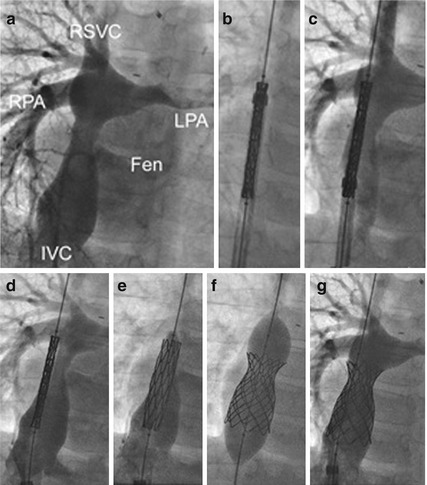
Fig. 8.1
Covered stent (Premounted Cheatham Platinum on a balloon-in-balloon) implantation into a lateral tunnel of an 8-year-old boy with exercise-induced cyanosis and protein-losing enteropathy. Angiogram in (a) shows a tunnel stenosis before the branch pulmonary arteries and a patent fenestration. After passing a long sheath over a stiff guide wire placed in the SVC, the stent is advanced (b). Angiography via the long sheath is used to position the stent (c, d). The inner balloon is inflated with angiography confirming position in the stenosis and continued flow across the fenestration (e) followed by the outer balloon (f). Final angiogram shows the fenestration to be occluded (g) and the stenosis dilated. Note the position and shortening of the stent between (d) and (f) so that the final position does not obstruct the right pulmonary artery. RSVC right superior vena cava, RPA right pulmonary artery, LPA left pulmonary artery, FEN fenestration, IVC inferior vena cava
8.3 Stent Features
Given the diversity of lesions and patient size range, a single type of stent does not suit all situations. Stent implantation is an art of picking the best device for a specific patient and condition. It is better to be experienced with a limited range of stents (Table 8.2) rather than trying to master all.
Table 8.2
Commonly used stents in congenital heart disease
Stent | Material | Cell design | Nominal diameter (potential) | Length (mm) | Sheath size (F) | Guide wire (″) | Mounting | Common usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Sinus-Superflex-DS | N | O | 7–9 | 12–20 | 4 | 0.018 | Self-expandable | Neonate and infant lesions |
Zilver 518 | N | C | 6–10 | 20–80 | 5–7 | 0.018 | Self-expandable | Neonate and infant lesions |
Palmaz Blue | Cc | C | 4–7 (12) | 12–24 | 4–5 | 0.014 | Aviator plus | Neonate and infant lesions |
5 | 0.018 | Slalom | ||||||
Genesis medium | Ss | C | 4–8 (12) | 12–24 | 5–6 | 0.018 | Slalom | Neonate and infant lesions |
6 | 0.035 | Opta Pro | ||||||
Unmounted | ||||||||
Formula 535 | Ss | O | 5–8 (20) | 12–30 | 5–6 | 0.035 | High-pressure balloon catheter | PAs, atrial septum, RVOT |
Genesis large | Ss | C | 5–10 (12) | 19–79 | 5–6 | 0.018 | Slalom | PAs, atrial septum, RVOT |
6–7 | 0.035 | Opta Pro | ||||||
Unmounted | ||||||||
Visi-Pro | Ss | O | 5–10 (14) | 12–57 | 6–7 | 0.035 | High-pressure balloon catheter | PAs, atrial septum, RVOT |
Valeo Lifestent | Ss | O | 6–10 (20) | 18–56 | 5–6 | 0.035 | High-pressure balloon catheter | PAs, atrial septum, RVOT |
Genesis XD | Ss | C | 10–12 (18) | 19–59 | 8 | Depending on the balloon catheter | Unmounted | Pulmonary arteries |
Double Strut LD | Ss | O | 9–12 (18) | 16–76 | 8 | Depending on the balloon catheter | Unmounted | Pulmonary arteries |
Mega LD | Ss | O | 9–12 (18) | 16–36 | 9 | Depending on the balloon catheter | Unmounted | Pulmonary arteries < div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|