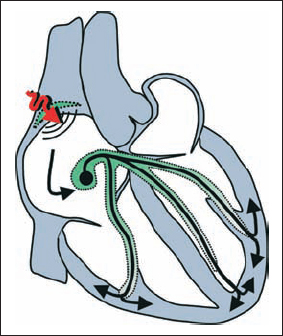
3.1 Sinus Arrythmias Mechanism:
Sinus Bradycardia
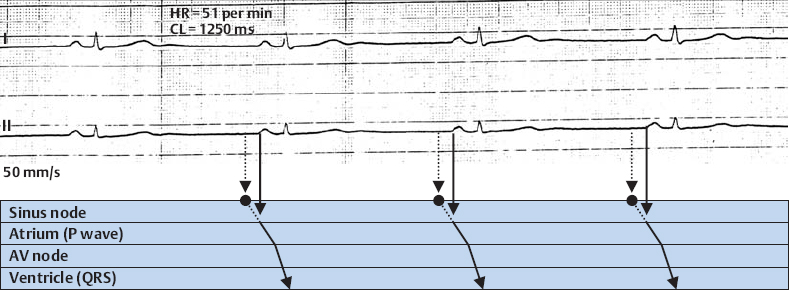
Sinus Bradycardia
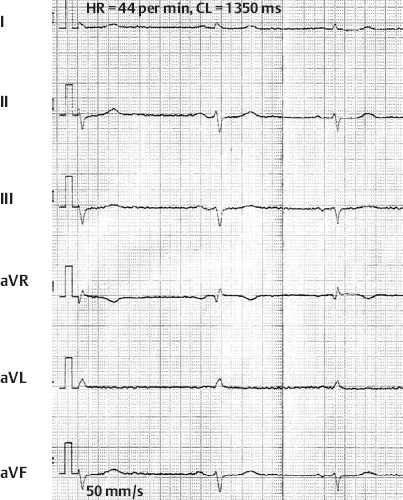
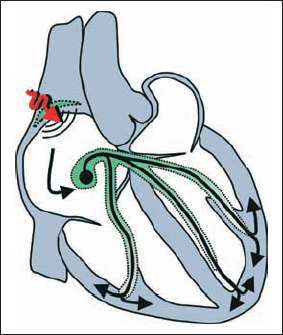
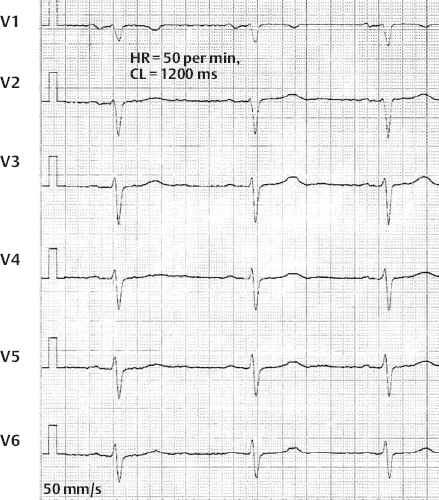
Sinus Bradycardia
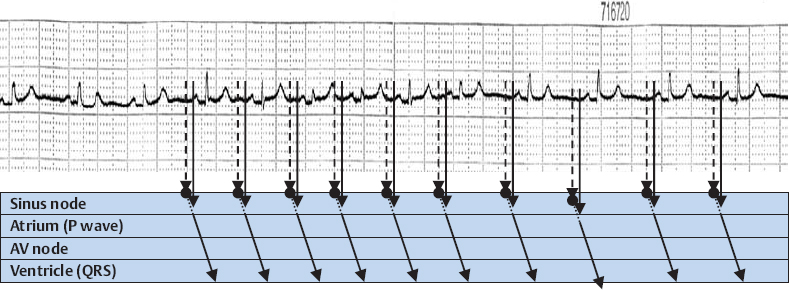
Sinus Arrhythmia
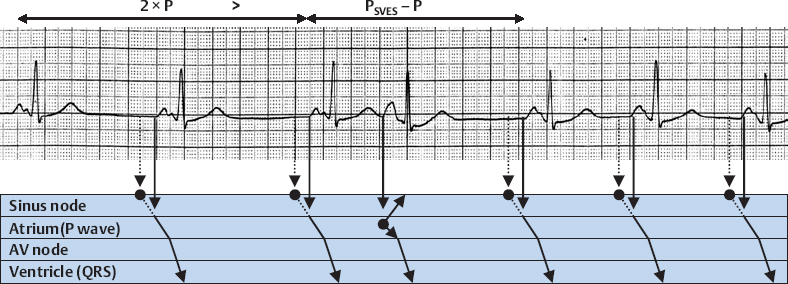
Postextrasystolic Pause Following SVES
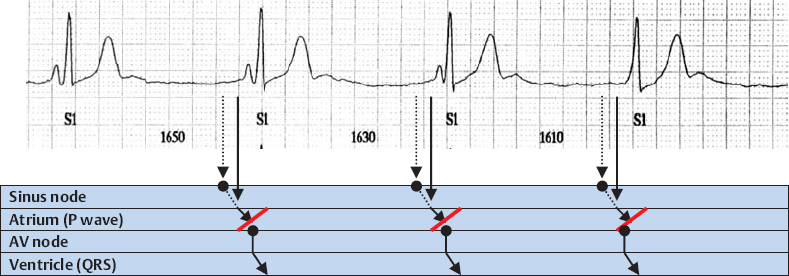
Sinus Bradycardia with AV Dissociation
AV Dissociation with Transition to Sinus Rhythm
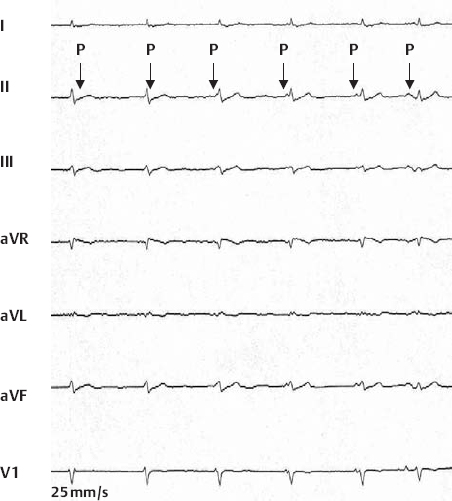
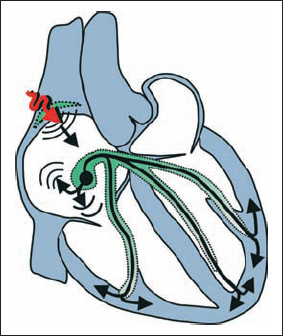
Deceleration of Sinus Node Frequency with Nodal Escape Rhythm
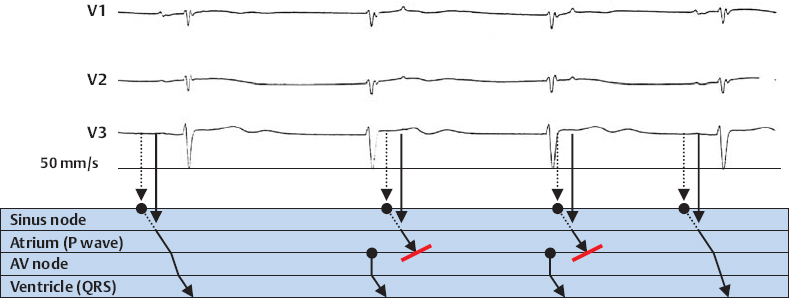
Deceleration of Sinus Node Frequency with Nodal Escape Rhythm
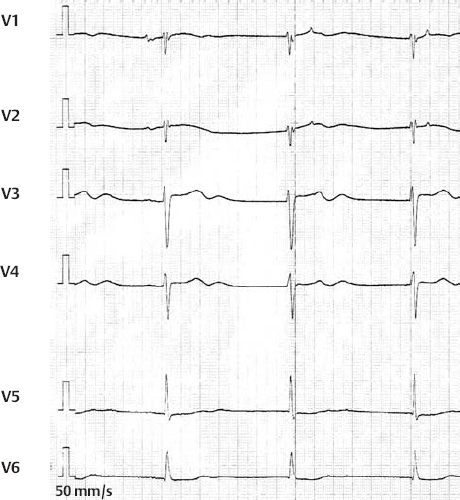
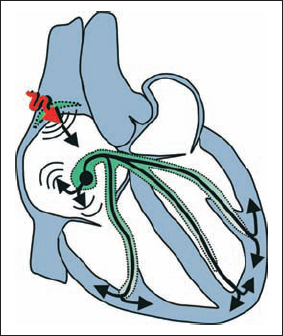
Sinoatrial 2nd Degree Block, Wenckebach Type
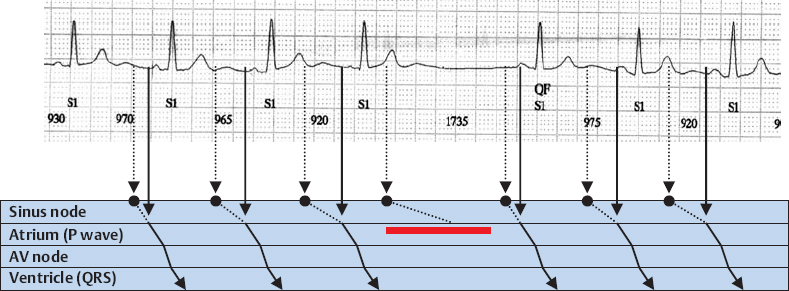
2nd Degree Sinoatrial Block, Wenckebach Type
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


