A The following measurements are made: 1. Calculate minute ventilation ( 2. If extra tubing with a volume of 250 mL were added to the system in a position such that it provided additional dead space, what would be the new VD/VT? 3. With the new system as described in Question 2, what would be the new PaCO2? 4. Going back to the original conditions (without added extra tubing), the ventilator settings are changed to new settings: a. Calculate the new b. What would happen to PaCO2 on the new settings? c. What would you expect PECO2 to be if you now measured it? 5. Using the original ventilator settings and arterial blood gases as given, calculate the alveolar-arterial difference in partial pressure of oxygen (AaDO2). 6. After the patient is improved, arterial blood gases measured with the patient breathing room air are as follows:
Sample Problems Using Respiratory Equations
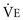 ), dead space–to–tidal volume ratio (VD/VT), alveolar volume (VA), and alveolar ventilation (
), dead space–to–tidal volume ratio (VD/VT), alveolar volume (VA), and alveolar ventilation (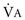 ).
).
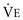 , VA,
, VA, 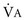 , and VD/VT.
, and VD/VT.
Sample Problems Using Respiratory Equations



