CHAPTER 15 Robot-Assisted Right Upper Lobectomy
Introduction
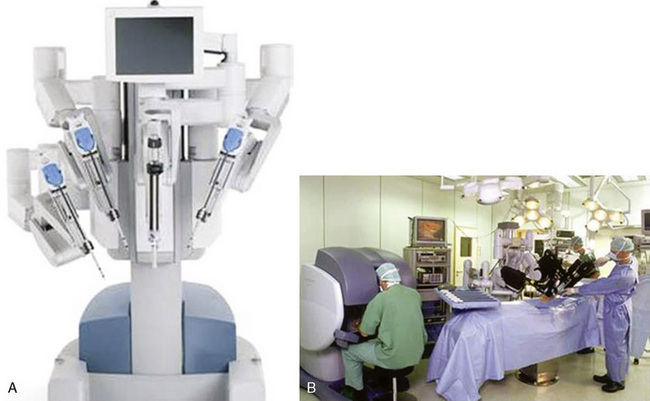
The da Vinci system (Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, Calif) has three components: an operating console for the surgeon; a praying mantis–like chassis, from which spring the robotic video unit and the three robotic arms; and the electronic communication tower system between the console and the chassis (Figure 15-1).
Approach to Robot-Assisted Right Upper Lobectomy
Key Points
♦ A ring clamp with a heavy sponge or Surgicel attached should be available for immediate use (Figure 15-2).
♦ Continuous intrathoracic carbon dioxide (CO2) insufflation is used to enhance the robotically assisted surgery. Keep the intrathoracic CO2 pressure less than 10–15 mm Hg to minimize a decrease in venous return and cardiac compliance.
♦ Avoid grasping the lung, hilar structures, or the airway with robotic instruments to minimize the risk of injury and bleeding. Non-robotic, less traumatic instruments are recommended to grasp the lung and will be discussed later in this chapter. The robotic instruments used are better suited for sweeping and very precise grasping.
Robot-Assisted Right Upper Lobectomy
Step 1. Patient Positioning
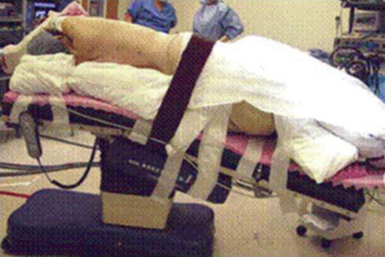
♦ The patient is placed in the lateral decubitus and reversed Trendelenburg position (Figure 15-3). This allows the diaphragm and intra-abdominal contents to drop away from the operative field to increase exposure and allows any bleeding that occurs to pool away from the operative field.
♦ The patient’s bed position is rotated 15 to 30 degrees posteriorly, and the head of the patient is directed toward the robotic chassis.
Step 2. Port Placement
♦ The target is the hilum, and the approximate location is drawn onto the patient’s chest; this is a 4-cm-diameter circle whose center is approximately 3 cm anterior and 2 cm cephalad to the tip of the scapula.
♦ The camera port (A) is placed in the eighth or ninth intercostal space (ICS) adjacent to the anterior costal margin. After the port is slowly placed in position, the pleural space is visualized to ensure there has been no damage to intrathoracic structures.
♦ CO2 is slowly infused to pressures of 10 to 15 mm Hg. If there is no evidence of pleural metastatic disease, the remaining thoracoports are placed.
♦ Place the thoracoports under direct intrapleural visualization to avoid injury to the neurovascular bundles and postoperative neuralgia.
♦ The most anterosuperior port site, usually in the anterior axillary to lateral clavicular line in the fourth ICS, serves as the utility port (F).
♦ The inferoanterior port, located in the anterior axillary line in the eighth to ninth ICS (B) and another port located in the posterior axillary line in the eighth to ninth ICS (E) are 8-mm ports used for the robotic arms. Both robotic ports are placed 10 to 12 cm on a lateral plane away from the camera port (A).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree