3.11 Reentry Tachycardia
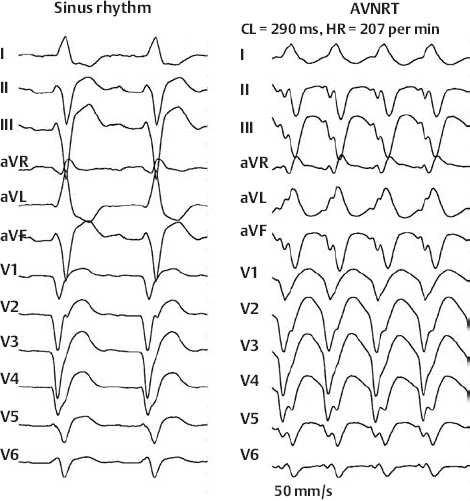
AV Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (Slow–Fast Type)
AV Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (Slow–Fast Type)
AV Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (Slow–Fast Type)
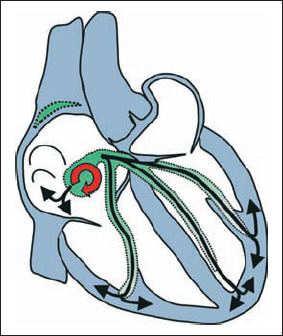
AV Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (Slow–Fast Type) With Left Bundle Branch Block
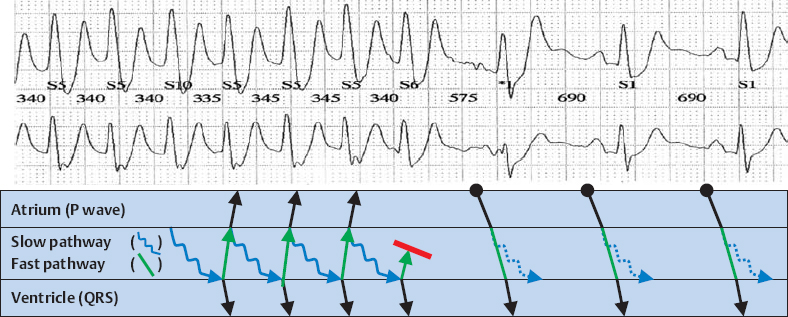
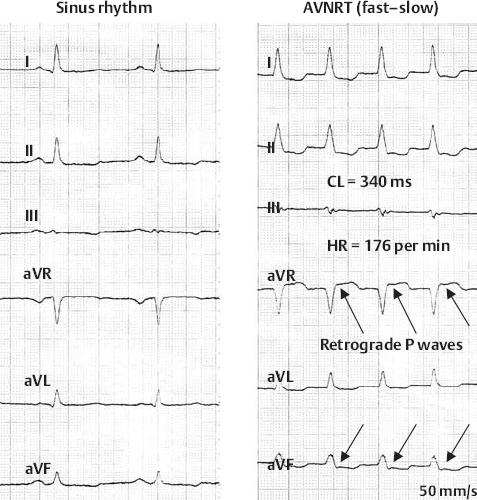
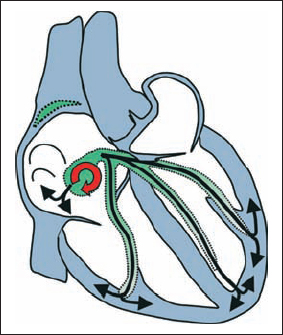
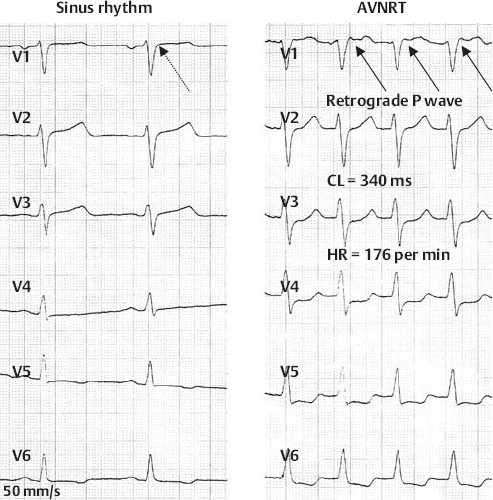
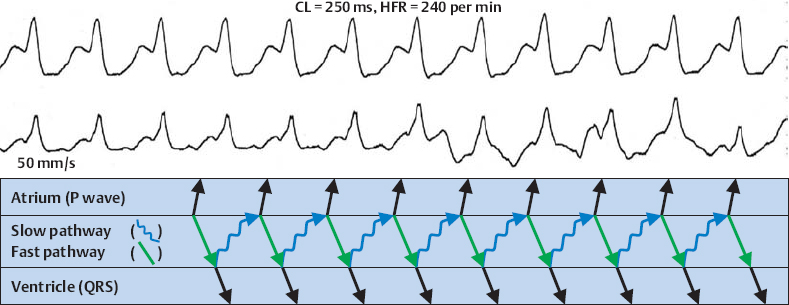
AV Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (Fast–Slow Type)
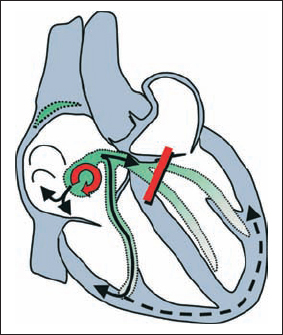
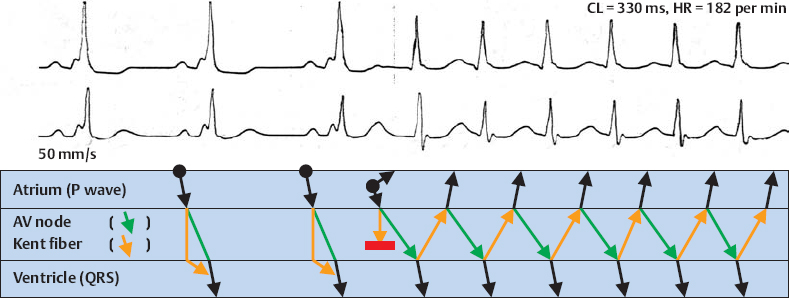
Orthodromic WPW Reentry Tachycardia With Nonconcealed WPW Syndrome
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


