Rapid Atrial Fibrillation
A 61-year-old man presents to the emergency room with atrial fibrillation and a rapid ventricular response.
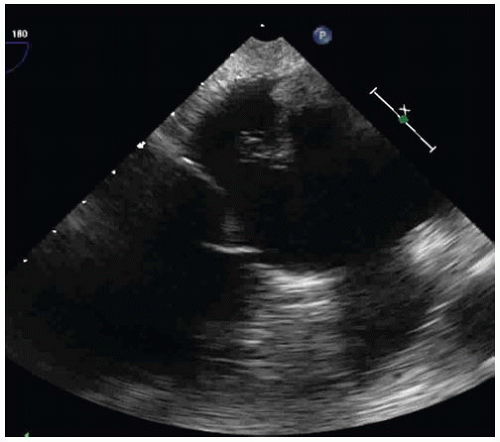
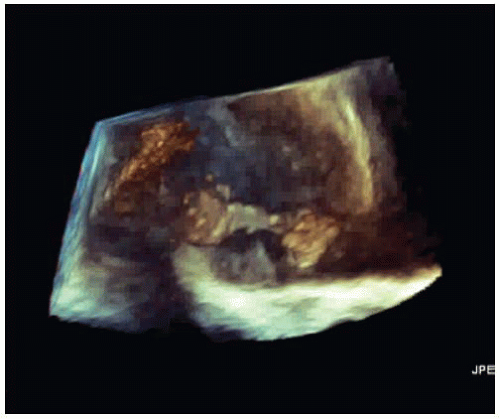
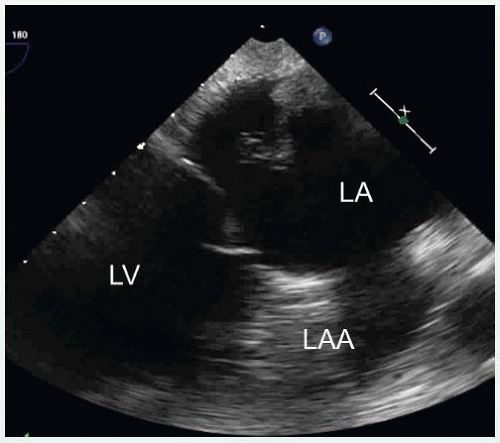
After anticoagulation and rate control, a transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) is performed prior to cardioversion (Figs. 42-1 and 42-2 and Videos 42-1 and 42-2).
QUESTION 1. All of the following would be appropriate except:
A. Continue anticoagulation
B. Perform direct current cardioversion
C. Obtain computed tomography surgery consultation
D. Order magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
View Answer
ANSWER 1: B. All but cardioversion would be appropriate. The left atrial (LA) appendage is clearly visualized and demonstrates no thrombus (Fig. 42-3). The mass is quite large and pedunculated and appears attached to the inferior aspect of the LA wall. This is a very unusual place for the most common LA tumor, myxoma. Therefore, in a patient with atrial fibrillation, LA thrombus is still a likely diagnosis.
QUESTION 2. The patient underwent cardiac MRI, which showed a nonenhancing lesion. All of the following would be appropriate except:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree