Pulmonary embolism (PE), frequently encountered as a cardiogenic shock and reversible right-sided heart failure following the obstruction of pulmonary artery and its branches mostly by trombus is a fatal disease requiring urgent intervention. We presented a case of acute Pulmonary embolism with Right Heart Trombus and hemodynamic instability, and successfully treated with systemic thrombolysis.
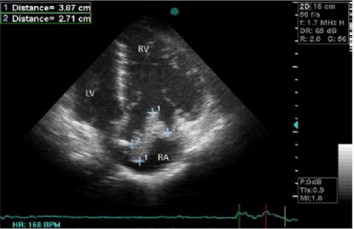
A 32 year- old female patient having no known disase presented to the emergency department with short of breath and feeling of palpitation for a day prior to admission. Seven days prior to admission, she had fallen from height, causing her a small amount of vaginal bleeding. The patient subsequently rested in immobilized form. Since she had severe pain as she was passing urine,she gave up getting fluid. On the 6th day of resting period with the complaint of shortness of breath and palpitation she was assesed in the emergency department.The blood pressure and the throbs of the patient were 90/60 mmhg and 130 b/m, respectively. There were 3/6 systolic murmur in heart sounds and bilateral basilar pulmonary rales. The first ECG showed a sinus rhythm. Arterial blood gas analysis show that hypoxemia with mild respiratory and metabolic alkalosis.A trans-thoracic echocardiogram(TTE) imaging study documented a large (dimensions 38×29 mm), serpentine, free-floating thrombus in the right atrium (figure 1). Laboratory testing showed D-dimer 12,374 ng/ml, troponin I 0,032 ng/ml, CKMB 18,7 ng/ml hgb:11,3mg/l, Wbc:14000/mm3, plt:350000/mm3, cre:11.3ng/ml, bun:156.
T-PA(tissue plasminogen activator) fibrinolytic therapy with alteplase was initiated the right atrial thrombus gradually reduced its size seen on t-TTE, and completely dissolved at 4 hour from the start of treatment.. During the following six hour, hemodynamic and respiratory conditions progressively improved and remained stable.
Venous thromboembolism (VTE), including pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis, is a major cause of morbidity and mortality.Early administration and diagnosis may be safe reduce the incidence of mortality in doubtfully patients.