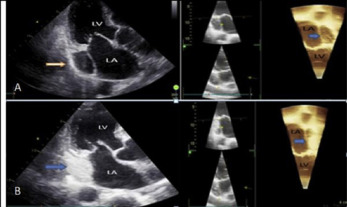
Persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC) is the most common congenital thoracic venous anomaly with a prevalence of 0.3–0.5%. PLSVC can be associated with other cardiovascular abnormalities such as atrial septal defect, bicuspid aortic valve, coarctation of aorta, coronary sinus ostial atresia, and cor triatriatum. A 81-year old male was admitted to syncope and palpitation. He had history of hypertension and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation Physical examination was normal. Cranial MRI was normal. 2D and 4D Transthoracic echocardiography revealed normal findings except a hugely dilated coronary sinus suggestive of a PLSVC in apical 4-chamber view (Figure1A). Agitated saline contrast study from the left antecubital vein demonstrated prior contrast enhancement of this giant coronary sinus before the right atrium on 2D and 4D transthoracic echocardiography(Figure1B). The patient was discharged with warfarin, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and beta-blocker.